Comparative Study of Biological Processes and Anatomy

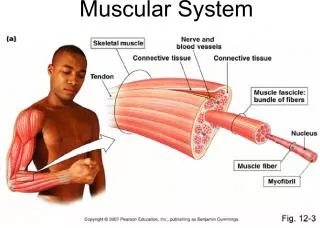
This study compares DNA replication, transcription, translation, and anatomy of various organisms including mammals, reptiles, fish, and birds at different levels of mutation distance.
- Uploaded on | 1 Views
-
 andrejlaurent
andrejlaurent
About Comparative Study of Biological Processes and Anatomy
PowerPoint presentation about 'Comparative Study of Biological Processes and Anatomy'. This presentation describes the topic on This study compares DNA replication, transcription, translation, and anatomy of various organisms including mammals, reptiles, fish, and birds at different levels of mutation distance.. The key topics included in this slideshow are . Download this presentation absolutely free.
Presentation Transcript
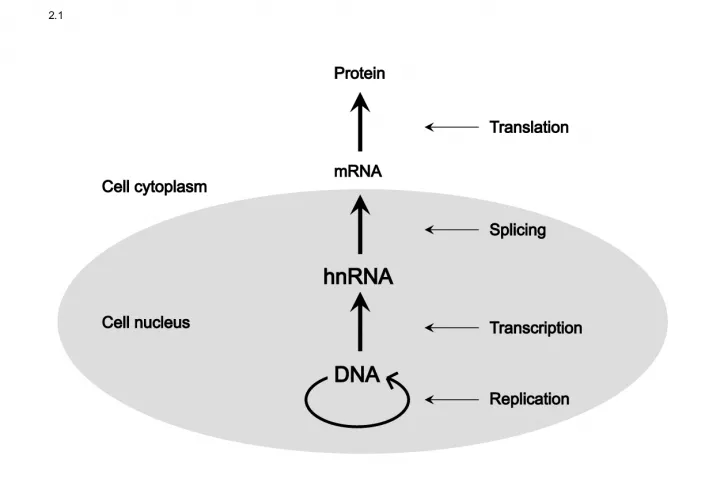
1. 2.1 DNA Replication Transcription hnRNA Splicing Translation Cell nucleus Cell cytoplasm mRNA Protein
2. 2.2 Average Minimal Mutation Distance 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 Candida Saccharomyces Neurospora Moth Screw worm Tuna Snake Turtle Penguin Chicken Duck Pigeon Kangaroo Rabbit Pig Donkey Horse Dog Monkey Man
3. 2.3 I II III Fish Salamander Tortoise Chick Hog Calf Rabbit Human
4. 2.4 Human Lizard Cat Whale Bat Frog Bird Humerus Ulna Radius Carpal 1 2 3 4 5 2 3 4 5 2 3 4 5 2 3 4 5 2 3 4 5 2 3 4 5 2 3 1 1 1 1 1 1
5. 2.5 Glyptodont (fossil) Armadillo (living)
6. 2.6
7. 2.7
8. 2.8 Generation 1, infants Generation 1, reproductive age Generation 2, infants Spread of successful variants through inheritance Differential death before reproduction Variability in developmental programs
9. 2.9 t 1 t 2 Biased sample Geographical barrier
10. 2.10 Transcription 3’ 5’ Stop codon Transcription starts here TATA box GC box CAAT box GC box Controls the start point of the transcription Controls the binding of RNA polymerase Promoter region: Controls the timing and tempo of transcription Exon 2 Exon 1 Intron 1
11. 2.11
12. 2.12 Crossing over of homologous chromosomes Paired chromosomes Inversion Deletion Insertion
13. 2.13
14. 2.14 (a) Stabilizing (b) Directional (c) Disruptive Frequency of Phenotypes