Understanding Mitosis and Cancer


To cure cancer, we must understand what causes it. This means comprehending how errors in mitosis can occur and lead to the proliferation of abnormal cells.
- Uploaded on | 4 Views
-
 emilieandersen
emilieandersen
About Understanding Mitosis and Cancer
PowerPoint presentation about 'Understanding Mitosis and Cancer'. This presentation describes the topic on To cure cancer, we must understand what causes it. This means comprehending how errors in mitosis can occur and lead to the proliferation of abnormal cells.. The key topics included in this slideshow are . Download this presentation absolutely free.
Presentation Transcript
1. Mitosis & Cancer: When Making New Cells Goes Terribly Wrong!
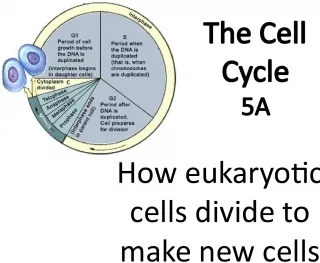
2. If we want to cure cancer… We must understand what causes it. This means understanding the cell cycle.
3. When is mitosis a good thing? 1) When you have to add or replace cells growth & development repair replacement
4. Checkpoints 2) There are strict checkpoints in the cell cycle to ensure that each stage does not start before the last one finished Checkpoint in Interphase: S phase to make sure that DNA was replicated correctly
5. When is mitosis a BAD thing 3) When cells reproduce & they are not needed these cells take over organs, but don ’ t do the right job they just keep making copies cancer damages organs
6. What is cancer 4) Cancer is a disorder in which some of the body ’ s own cells lose the ability to control growth Cancer cells do not respond to the signals that regulate the growth of most cells
7. How do the cells turn bad? The timing of the cell cycle is regulated by cyclins (proteins) Cyclins trigger cell division For example: p53 gene regulates the process that leads the cell into mitosis Conditions have to be right for the cell to divide 5) Gene proto-oncogenes encourage cell division in normal healthy cells 6) Tumor suppressor genes inhibit cell division
8. Why would cells just make copies? 7) If DNA gets damaged, cells stop listening to correct instructions mutations Causes of mutations: UV radiation chemical exposure radiation exposure heat cigarette smoke pollution age genetics
9. 8) Cells gone bad… If the proto-oncogene is damaged then cells can either never divide or divide uncontrollably creating a tumor If the tumor-suppressor gene gets damage it may never tell the cell to stop dividing and the cell will divide and divide creating a tumor
10. Tumors 9) Benign tumor abnormal cells remain at original site as a lump most do not cause serious problems & can be removed by surgery
11. Tumors 10) Malignant tumor cells leave original site carried by blood system to other tissues start more tumors damage functions of organs throughout body
12. Treatments for cancers 11) Treatments kill rapidly dividing cells chemotherapy poisonous drugs that kill rapidly dividing cells radiation high energy beam kills rapidly dividing cells side effects
13. 2009-2010 Any Questions?? Any Questions??