Cell Structure and Function: A Historical Overview


This chapter provides an overview of the historical contributions to the understanding of cell structure and function. Starting with the observations of Anton van Leeuwenhoek and Robert Hooke in the
- Uploaded on | 1 Views
-
 hazeljohnson
hazeljohnson
About Cell Structure and Function: A Historical Overview
PowerPoint presentation about 'Cell Structure and Function: A Historical Overview'. This presentation describes the topic on This chapter provides an overview of the historical contributions to the understanding of cell structure and function. Starting with the observations of Anton van Leeuwenhoek and Robert Hooke in the. The key topics included in this slideshow are . Download this presentation absolutely free.
Presentation Transcript
Slide1CELL STRUCTURE& FUNCTION Chapter 7 – Part 1 CP Biology Paul VI Catholic High School
Slide2CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTIONHISTORY: 1600’S Anton van Leeuwenhoek 1665 Robert Hooke 1838 Matthias Schleiden 1839 Theodor Schwann 1855 Rudolph Virchow
Slide3CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTIONAnton van Leeuwenhoek
Slide4CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTIONRobert Hooke 1665
Slide5CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTIONMatthias Schleiden 1838
Slide6CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTIONTheodor Schwann 1839
Slide7CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTIONRudolf Virchow 1855
Slide8CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTIONCELL THEORY: 1. All living things are composed of cells 2. Cells are the basic unit of structure & function in living things 3. New cells are produced from pre-existing cells
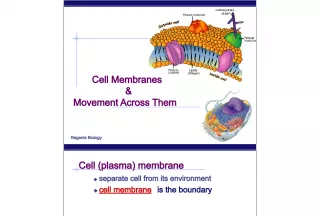
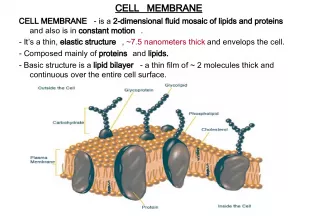
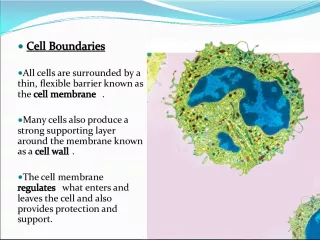
Slide9CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTIONBASIC CELL STRUCTURE: ALL Cells have: Cell Membrane Cytosol
Slide10CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTIONSOME CELLS HAVE : Nucleus Cytoplasm
Slide11CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTIONCELL CATEGORIES: EUKARYOTIC CELLS (Eukaryotes) PROKARYOTIC CELLS (Prokaryotes)
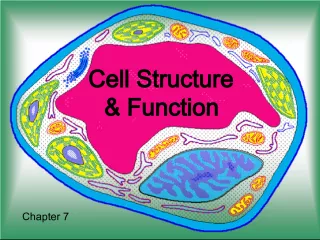
Slide12CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTIONEUKARYOTES: • Contain nucleus • Have Cell Membrane • Cytoplasm • Organelles • Include Plant, Animal, Fungi, and many Microorganisms
Slide13CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTION
Slide14CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTION
Slide15CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTIONPROKARYOTES: • Smaller, Simpler Cells • Cell Membranes • NO Nuclei • ALL Bacteria are Prokaryotes Examples - • E. coli • S. Aureus
Slide16CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTIONCELL SIZE Average Cell 5-50 μ m Surface Area 4 π r 2 Volume 4/3 π r 3 Cell Surface is interface between internal and external environment
Slide17CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTIONA small cell has a greater ratio of surface area to volume than a large cell of the same shape. – This ratio limits cell size!
Slide18CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTIONCELL STRUCTURES: 1. CELL WALL : • Found in Plants, Algae, Fungi and many Prokaryotes • Function - Support & Protection • External to Cell Membrane
Slide19CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTION1a. BACTERIAL CELL WALL: Characteristics: P eptidoglycan Gram + (Violet/Blue) Gram – (Red/Pink) Encapsulated
Slide20CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTION
Slide21CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTION
Slide22CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTION1b. PLANT CELL WALLS : Green Plants - Primary Cellulose Woody Plants - Secondary Lignin
Slide23CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTION
Slide24CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTION(CELL STRUCTURES - cont’d) 2. NUCLEUS Robert Brown (1831) Chromatin/Chromosome Nucleoplasm Nucleolus Nuclear Envelope
Slide25CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTIONBrown’s Microscope Robert Brown
Slide26CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTION
Slide27CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTION
Slide28CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTION
Slide29CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTION
Slide30CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTION
Slide31CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTIONAdditional Organelles: You are responsible for the name, structure, function and visual recognition of the following organelles: 3. Ribosome 4. Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) Smooth ER Rough ER 5. Golgi Apparatus 6. Vacuole 7. Lysosome 8. Mitochondrion 9. Chloroplast
Slide32CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTIONNucleus Smooth endoplasmic reticulum Rough endoplasmic reticulum Ribosomes Golgi apparatus Plasma membrane Mitochondrion Flagellum Not in most plant cells Lysosome Centriole Microtubule Cytoskeleton Intermediate filament Microfilament Peroxisome
Slide33CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTIONCentral vacuole Not in animal cells Chloroplast Cell wall Golgi apparatus Nucleus Microtubule Cytoskeleton Intermediate filament Microfilament Ribosomes Smooth endoplasmic reticulum Mitochondrion Peroxisome Plasma membrane Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Slide34CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTIONCYTOSKELETON: a. Microtubules b. Intermediate filaments c. Actin filaments /M icrofilaments * Know Structure and function of each
Slide35CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTIONLong, thin fibers “String of Pearls” Concentrated in Cortex Amoeboid Motion Most durable “Rope-like” Structure Provide Stability (vimentin) Hollow tube MTOC Strengthen Cell Stabilize cell relative to other cells
Slide36CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTIONA. Microtubules Functions – • Structural Role • Movement of Chromosomes • Structural Component of Cilia and Flagella • Track for motor proteins
Slide37CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTIONPlus End (+) Away from MTOC (Toward Nucleus) Minus End (-) Toward the MTOC A. Microtubules
Slide38CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTIONINTRACELLULAR MOTOR MOLECULES E xamples- KINESIN: Move Organelles toward (+) end DYNEIN: Move Organelles toward (-) end Kinesin Walking YouTube The inner Life of the Cell Video
Slide39CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTION
Slide40CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTION
Slide41CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTIONB. Intermediate Filaments: Function - Strengthen Cell Stabilize Position organelles Stabilize cell relative to other cells
Slide42CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTION C. Actin filaments (Microfilaments) Function : • Anchor Cytoskeleton to cell membrane • Determine consistency of cytoplasm • Interact with Myosin (motor molecule) for muscle contraction Muscle Contraction Video
Slide43CELL STRUCTURE &FUNCTION
Slide44CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTIONCELL MOVEMENT: 1. Crawling: Actin/Myosin Gel-Sol States Pseudopod Formation 2. Pinching Actin filaments Animal cells Cytokinesis
Slide45CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTION
Slide46CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTIONAmoeba
Slide47CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTION
Slide48CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTION
Slide49CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTIONCytokinesis of Animal Cell
Slide50CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTIONActin filament causing cell separation
Slide51CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTIONCELL MOVEMENT: 3. Prokaryote Flagella Protein Structure (flagellin) Rotatory Movement Molecular motor in cell wall Basal Apparatus Hook Filament
Slide52CELL STRUCTURE &FUNCTION
Slide53CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTIONCELL MOVEMENT: 4. Eukaryote Flagella Microtubular Structure 9+2 Arrangement Basal Body Origin 9 “triplet” structure “Whip-like” motion
Slide54CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTION“9+2” arrangement microtubules
Slide55CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTION
Slide56CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTIONCELL MOVEMENT: 5. Cilia Many, Short, often in rows Internal structure like flagella Multiple functions
Slide57CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTIONStructure Of Cilia