Understanding the pH Scale and Its Applications

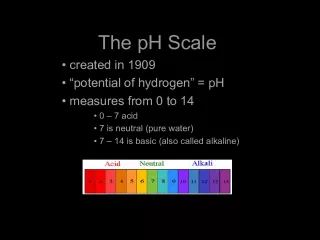
The pH scale is a widely used standard measurement for determining the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) in a solution. Neutral solutions have a pH of 7, which is equivalent to pure water
- Uploaded on | 0 Views
-
 magarete
magarete
About Understanding the pH Scale and Its Applications
PowerPoint presentation about 'Understanding the pH Scale and Its Applications'. This presentation describes the topic on The pH scale is a widely used standard measurement for determining the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) in a solution. Neutral solutions have a pH of 7, which is equivalent to pure water. The key topics included in this slideshow are . Download this presentation absolutely free.
Presentation Transcript
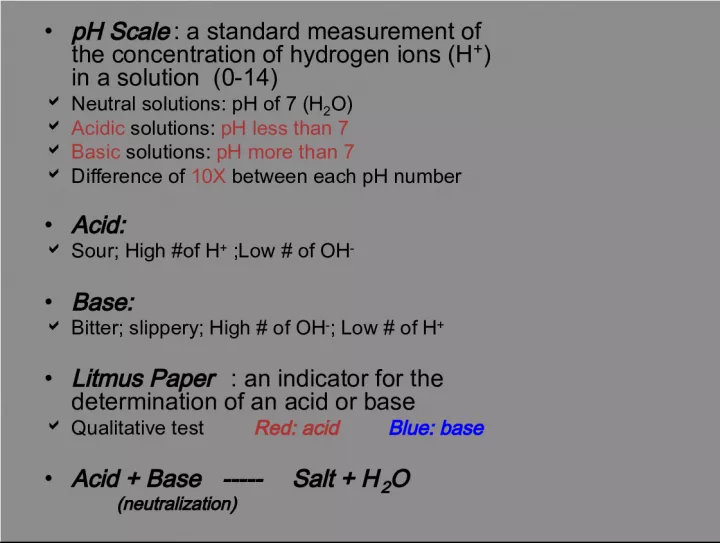
Slide1•pH Scale : a standard measurement of the concentration of hydrogen ions (H + ) in a solution (0-14) Neutral solutions: pH of 7 (H 2 O) Acidic solutions: pH less than 7 Basic solutions: pH more than 7 Difference of 10X between each pH number • Acid: Sour; High #of H + ;Low # of OH - • Base: Bitter; slippery; High # of OH - ; Low # of H + • Litmus Paper : an indicator for the determination of an acid or base Qualitative test Red: acid Blue: base • Acid + Base ----- Salt + H 2 O (neutralization)
Slide2•Physical Change : appearance changes slightly; still recognizable • Chemical Change : rearrangement of atoms ; appearance totally changed • Chemical Equation : describes a chemical reaction A + B ------ C + D Reactants ------ Products • Law of the Conservation : During a chemical reaction, mass (energy) is neither created nor destroyed. • Inorganic Compound : No carbon is present Example: H 2 O
Slide3•Organic Compound : Carbon is present ; found in living things; shown by structural formula • Isomers : compounds with the same chemical formula but different structural formulas ; with different physical and chemical properties • Carbohydrates : (end in OSE) • Give quick energy ; contain C,H,O (2H:O); sugars, starches • Monosaccharides : C 6 H 12 O 6 (simple sugars) Examples : glucose (commercial name of dextrose), galactose, fructose (in fruit) Isomers: glucose, fructose, galactose
Slide4•Disaccharides : C 12 H 22 O 11 (double sugars) Examples : maltose, sucrose (table sugar), lactose (milk sugar) Isomers: maltose, sucrose, lactose Dehydration Synthesis Reactions: A + B ----- C + H 2 O (H 2 O out) Hydrolysis Reaction: C + H 2 O ------ A + B (H 2 O in) Glucose + Glucose ------ Maltose + H 2 O C 6 H 12 O 6 + C 6 H 12 O 6 ------- C 12 H 22 O 11 + H 2 O Glucose + Fructose ----- Sucrose + H 2 O C 6 H 12 O 6 + C 6 H 12 O 6 ------- C 12 H 22 O 11 + H 2 O
Slide5Glucose + Galactose ------ Lactose + H 2 O C 6 H 12 O 6 + C 6 H 12 O 6 ------ C 12 H 22 O 11 + H 2 O --------------------------------------------------------------------------- Maltose + H 2 O -------- Glucose + Glucose C 12 H 22 O 11 + H 2 O ------- C 6 H 12 O 6 + C 6 H 12 O 6 Sucrose + H 2 O ------- Glucose + Fructose C 12 H 22 O 11 + H 2 O ------- C 6 H 12 O 6 + C 6 H 12 O Lactose + H 2 O ------ Glucose + Galactose C 12 H 22 O 11 + H 2 O ------ C 6 H 12 O 6 + C 6 H 12 O 6 • Polysaccharides : starch (complex sugars) Cellulose (plant starch) Glycogen (animal starch); stored in the liver
Slide6•Test for Monosaccharides: Benedict’s Solution (blue solution) is added to an unknown substance + heat Results : green, orange, brown (+) for monosaccharides; blue (-) for disaccharides, polysaccharides A qualitative test • Test for Polysaccharides: Iodine (brown solution) is added to an unknown substance Results : black, blue (+) for polysaccharides; brown (-) for monosaccharides and disaccharides A qualitative test
Slide7•Lipids: • Gives stored energy ; contains C,H,O (H:O greater than 2:1); never dissolve in H 2 O Examples : oils (liquid), waxes (solid) • Body : padding around organs, insulation under skin Glycerol + 3 Fatty Acids -------- Lipid + 3 H 2 O Lipid + 3 H 2 O ------- Glycerol + 3 Fatty Acids • Types of Fats: Saturated Fat (bad) -C-C- Unsaturated Fat C=C Polyunsaturated Fat (good) C=C=C
Slide8•Cholesterol : clogs arteries • Steroids : important for growth, hormones • Proteins: • For maintenance and repair ; contain C,H,O,N • Another name for a protein: polypeptide chain • Bonds in a protein: peptide bonds Examples: antibodies, hormones, enzymes Enzyme: speeds up chemical reactions; also called catalyst , end in ASE • Amino Acids = “the building blocks of proteins”
Slide9Amino Acid + Amino Acid ----- Protein + H 2 O Protein + H 2 O ------- Amino Acid + Amino Acid • Parts of a Protein : COOH (carboxyl group) NH 2 amino group) • Lipoproteins (lipids and proteins in blood) HDL (high density lipoproteins): Remove cholesterol (+) LDL (low density lipoproteins): Produce cholesterol (-)