Proving Theorems Involving Rectangles
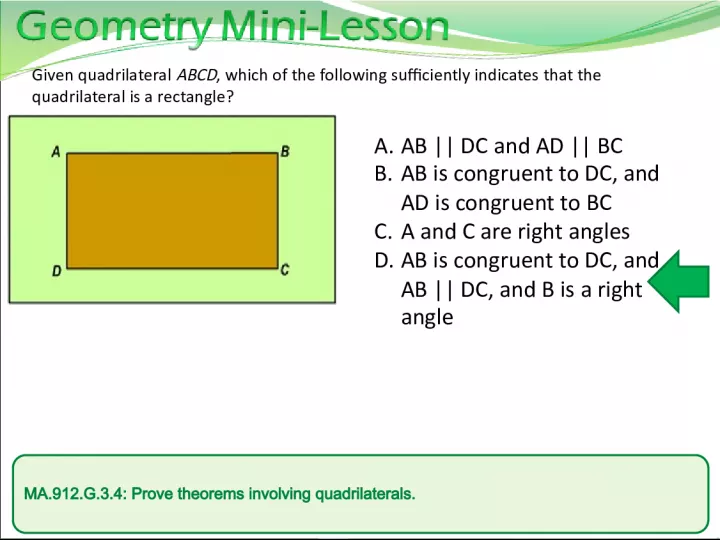

The article explores various theorems related to rectangles and how they can be proven. A quadrilateral ABCD is given and different conditions are presented to indicate that it is a
- Uploaded on | 0 Views
-
 pozvizdacis
pozvizdacis
About Proving Theorems Involving Rectangles
PowerPoint presentation about 'Proving Theorems Involving Rectangles'. This presentation describes the topic on The article explores various theorems related to rectangles and how they can be proven. A quadrilateral ABCD is given and different conditions are presented to indicate that it is a. The key topics included in this slideshow are . Download this presentation absolutely free.
Presentation Transcript
Slide2ma.912.g.3.4: prove theorems involving quadrilaterals.Given quadrilateral ABCD , which of the following sufficiently indicates that the quadrilateral is a rectangle? A. AB || DC and AD || BC B. AB is congruent to DC, and AD is congruent to BC C. A and C are right angles D. AB is congruent to DC, and AB || DC, and B is a right angle
Slide3ma.912.g.3.4: prove theorems involving quadrilaterals.Which statement is FALSE? A. Every square is a rhombus. B. All rectangles are parallelograms. C. The diagonals of all parallelograms bisect each other. D. Every property of a square is also a property of a parallelogram.
Slide4ma.912.g.3.4: prove theorems involving quadrilaterals.Figure JKLM is a rhombus. The measure of angle JKM is (2 x + 17)° and the measure of angle LKM is (3 x − 19)°. Which statement best explains why the equation 2 x + 17 = 3 x − 19 can be used to find x ? A. All sides of a rhombus are congruent. B. Opposite angles in a rhombus are congruent. C. The diagonals of a rhombus are perpendicular. D. The diagonals of a rhombus bisect opposite angles.
Slide5ma.912.g.3.4: prove theorems involving quadrilaterals.Jasmine is about to buy a rectangular plot of land to build her house. Before she buys it, she wants to verify the shape is truly rectangular. Which of the following methods should she use to prove the plot of land is a rectangle? A. Verify that the diagonals of the plot of land are congruent. B. Verify that opposite sides of the plot of land are congruent. C. Verify that the diagonals of the plot of land bisect each other. D. Verify that consecutive angles of the plot of land are supplementary.
Slide6ma.912.g.3.4: prove theorems involving quadrilaterals.Given a rhombus, which statement is FALSE? A. The diagonals are perpendicular. B. The diagonals bisect each other. C. Exactly one pair of opposite sides is parallel. D. Both pairs of opposite angles are congruent.
Slide7ma.912.g.3.4: prove theorems involving quadrilaterals.Figure STUV is a parallelogram. The measure of angle S is (5 x + 13)° and the measure of angle T is (7 x − 40)°. Which statement best explains why the equation 5 x + 13 + 7 x − 40 = 180 can be used to find x ? A. Opposite sides of a parallelogram are parallel. B. Opposite angles in a parallelogram are congruent. C. Consecutive angles in a parallelogram are supplementary. D. Consecutive angles in a parallelogram are complementary.
Slide8ma.912.g.3.4: prove theorems involving quadrilaterals.
Slide9ma.912.g.3.4: prove theorems involving quadrilaterals.Miguel thinks the shape of his math classroom is a square. Tom disagrees. He thinks the classroom is rectangular but not square. Which of the following methods should Miguel use to prove his rectangular math classroom is truly square? A. Verify the diagonals of the classroom are perpendicular. B. Verify that opposite sides in the classroom are congruent. C. Verify that the diagonals of the classroom are congruent. D. Verify that the diagonals of the classroom bisect each other.




















