Understanding Lipids: Fats & Oils in AP Biology


This article revolves around the concept of lipids in AP Biology, specifically focusing on fats and oils. Lipids are long-term energy storage molecules that provide concentrated energy.
- Uploaded on | 1 Views
-
 romy
romy
About Understanding Lipids: Fats & Oils in AP Biology
PowerPoint presentation about 'Understanding Lipids: Fats & Oils in AP Biology'. This presentation describes the topic on This article revolves around the concept of lipids in AP Biology, specifically focusing on fats and oils. Lipids are long-term energy storage molecules that provide concentrated energy.. The key topics included in this slideshow are . Download this presentation absolutely free.
Presentation Transcript
Slide1AP BiologyLipids: Fats & Oils
Slide2AP Biology2006-2007 Lipids long term energy storage concentrated energy
Slide3AP BiologyLipids Lipids are composed of C, H, O long hydrocarbon chains (H-C) “Family groups” fats phospholipids steroids Do not form polymers big molecules made of smaller subunits not a continuing chain
Slide4AP BiologyFats Structure: glycerol (3C alcohol) + fatty acid fatty acid = long HC “tail” with carboxyl (COOH) group “head” dehydration synthesis H 2 O enzyme
Slide5AP BiologyBuilding Fats Triacylglycerol 3 fatty acids linked to glycerol ester linkage = between OH & COOH hydroxyl carboxyl
Slide6AP BiologyDehydration synthesis dehydration synthesis H 2 O H 2 O H 2 O H 2 O enzyme enzyme enzyme
Slide7AP BiologyFats store energy Long HC chain polar or non-polar? hydrophilic or hydrophobic? Function: energy storage concentrated all H-C ! 2x carbohydrates cushion organs insulates body think whale blubber! Why do humans like fatty foods?
Slide8AP BiologySaturated fats All C bonded to H No C=C double bonds long, straight chain most animal fats solid at room temp. contributes to cardiovascular disease (atherosclerosis) = plaque deposits
Slide9AP BiologyUnsaturated fats C=C double bonds in the fatty acids plant & fish fats vegetable oils liquid at room temperature the kinks made by double bonded C prevent the molecules from packing tightly together mono-unsaturated? poly-unsaturated?
Slide10AP BiologySaturated vs. unsaturated saturated unsaturated
Slide11AP BiologyPhospholipids Structure: glycerol + 2 fatty acids + PO 4 PO 4 = negatively charged It’s just like a penguin… A head at one end & a tail at the other !
Slide12AP BiologyPhospholipids Hydrophobic or hydrophilic? fatty acid tails = PO 4 head = split “personality” interaction with H 2 O is complex & very important ! “repelled by water” “attracted to water” Come here, No, go away ! Come here, No, go away ! hydrophobic hydrophillic
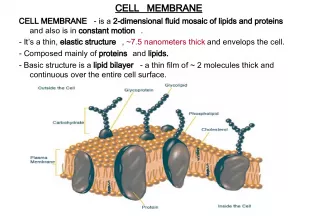
Slide13AP BiologyPhospholipids in water Hydrophilic heads “attracted” to H 2 O Hydrophobic tails “hide” from H 2 O can self-assemble into “bubbles” bubble = “micelle” can also form a phospholipid bilayer early evolutionary stage of cell? bilayer water water
Slide14AP BiologyWhy is this important? Phospholipids create a barrier in water define outside vs. inside they make cell membranes ! Tell them about soap !
Slide15AP BiologySteroids Structure: 4 fused C rings + ?? different steroids created by attaching different functional groups to rings different structure creates different function examples: cholesterol, sex hormones cholesterol
Slide16AP BiologyCholesterol Important cell component animal cell membranes precursor of all other steroids including vertebrate sex hormones high levels in blood may contribute to cardiovascular disease
Slide17AP BiologyCholesterol helps keep cell membranes fluid & flexible Important component of cell membrane
Slide18AP BiologyFrom Cholesterol Sex Hormones What a big difference a few atoms can make!
Slide19AP Biology2006-2007 Let’s build some Lipids!
Slide20AP Biology2007-2008 Ghosts of Lectures Past (storage)
Slide21AP BiologyPhospholipids & cells Phospholipids of cell membrane double layer = bilayer hydrophilic heads on outside in contact with aqueous solution outside of cell and inside of cell hydrophobic tails on inside form core forms barrier between cell & external environment Tell them about soap !