Organization of Cell Membrane


Learn how cell membrane is organized through completing a handout and explaining the functions of nucleolus, ribosomes, endoplasmic reticulum, cytoplasm, and the plasma membrane. Discover how the flexible membrane enables unicellular organisms to move.
- Uploaded on | 1 Views
-
 sannipesola
sannipesola
About Organization of Cell Membrane
PowerPoint presentation about 'Organization of Cell Membrane'. This presentation describes the topic on Learn how cell membrane is organized through completing a handout and explaining the functions of nucleolus, ribosomes, endoplasmic reticulum, cytoplasm, and the plasma membrane. Discover how the flexible membrane enables unicellular organisms to move.. The key topics included in this slideshow are . Download this presentation absolutely free.
Presentation Transcript
Slide1Aim: How cell membrane organized?HW #10 1. Complete the handout on the cell Do now: You have 5 min. 1. Explain how the following structures: a. Nucleolus b. Ribosomes c. Endoplasmic reticulum d. cytoplasm
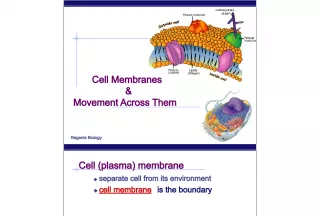
Slide2*The Plasma Membrane
Slide3*Photograph of a Cell Membrane
Slide4I. Cell MembraneA. General 1. Flexible and allows a unicellular organism to move
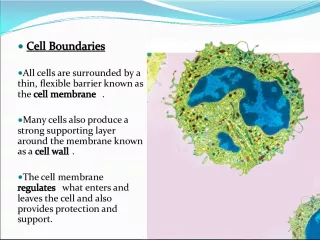
Slide51.Maintain a high concentration of materials in the cell. 2. Keep harmful materials out. 3. Control the movement of materials into and out of the cell. 4. Let the cell sense its environment. B. Function
Slide6 5. Protective barrier 6. Regulate transport in & out of cell (selectively permeable) 7. Allow cell recognition 8. Provide anchoring sites for filaments of cytoskeleton
Slide7Membrane Components
Slide8Proteins Are Critical to Membrane Function
Slide99. Provide a binding site for enzymes10. Interlocking surfaces bind cells together 11. Contains the cytoplasm (fluid in cell)
Slide10C. Maintains homeostasis1. Balanced internal condition of cells. Also called equilibrium 2. Maintained by plasma membrane controlling what enters & leaves the cell.
Slide11Review1. Explain what would happen to a cell if the cell membrane did not do its job properly.
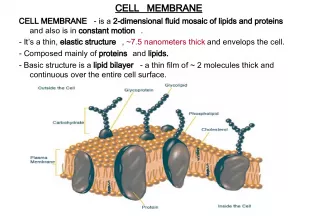
Slide12*D. Structure of the Cell Membrane
Slide13PhospholipidsCholesterol Proteins (peripheral & integral) Carbohydrates (glucose) 1. Membrane Components
Slide14*a. Phospholipids 1. Make up the cell membrane a. Contains 2 fatty acid chains that are nonpolar b. Head is polar & contains a –PO 4 group
Slide191. fluid- because individual phospholipids and proteinscan move around freely within the layer, like it’s a liquid. 2. MOSAIC- because of the pattern produced by the scattered protein molecules when the membrane is viewed from above. FLUID MOSAIC MODEL
Slide20Polar heads are hydrophilic “water loving”Nonpolar tails are hydrophobic “water fearing” Cell Membrane Makes membrane “Selective” in what crosses
Slide22Cell MembraneHydrophobic molecules pass easily ; hydrophillic DO NOT The cell membrane is made of 2 layers of phospholipids called the lipid bilayer
Slide23Solubility• Materials that are soluble in lipids can pass through the cell membrane easily
Slide24*Small molecules and larger hydrophobic molecules move through easily. e.g. O 2 , CO 2 , H 2 O Semipermeable Membrane
Slide25*Ions , hydrophilic molecules larger than water, and large molecules such as proteins do not move through the membrane on their own. Semipermeable Membrane