Key Figures in Psychology


Learn about the key figures in psychology, including Stanley Milgram, Ivan Pavlov, and Jean Piaget. Discover their groundbreaking research and contributions to the field of psychology.
- Uploaded on | 0 Views
-
 sinarath
sinarath
About Key Figures in Psychology
PowerPoint presentation about 'Key Figures in Psychology'. This presentation describes the topic on Learn about the key figures in psychology, including Stanley Milgram, Ivan Pavlov, and Jean Piaget. Discover their groundbreaking research and contributions to the field of psychology.. The key topics included in this slideshow are Psychology, Stanley Milgram, Obedience, Ivan Pavlov, Classical Conditioning, Jean Piaget, Child Development, Stages, Assimilation, Accommodation,. Download this presentation absolutely free.
Presentation Transcript
1. Who are these people? AP Psych Review Questions
2. Stanley Milgrim Studied obedience Two subjects (the teacher and the Learner). The teacher was told to shock the learner every time they answered the question incorrectly to see how far they were willing to go.
3. Ivan Pavlov Studied Classical conditioning Paired a bell with food to make the dog salivate.
4. Jean Piaget Child development occurs in stages. Sensorimotor, pre-operational, concrete operational, formal operational. Assimilation & Accommodation Conservation
5. Carl Rogers Humanistic Psychologist Client Centered Therapy Unconditioned Positive Regard
6. Hermann Rorshach Inkblot test Projective test
7. Julian Rotter Locus of control Socio-cultural Perspective of personality
8. Martin Seligman Positive psychology Learned helplessness Created the fear theory: we are prepared by evolution to readily develop fears to certain biologically relevant stimuli: spiders & snakes Explanatory style
9. Hans Selye GAS Theory (General Adaptation Syndrome): alarm, resistance, exhaustion Studied how stress affects the body
10. Walter Cannon Flight or fight response Cannon-Bard Theory of emotion
11. B. F. Skinner Behaviorist Studied operant conditioning with rats & pigeons Skinner Box
12. Charles Spearman g factor =general intelligence
13. Robert Sternberg Triangular theory of love
14. Lewis Terman Revised Binets intelligence test to help create the Stanford-Binet Intelligence Scales for use in the United States
15. Edward Thorndike Learning theorist Law of Effect-the probability of a response is altered by the effect it has, acts are reinforced tend to be repeated. Skinner based his work on Thorndikes.
16. Edward Titchener Carried Wundts ideas into the U.S. and called them Structualism
17. John B. Watson Behaviorist Conducted the Little Albert experiment Objected to the study of the mind, introspection is unscientificonly study that to which you observe.
18. Wilhelm Wundt Father of psychology Set up the drist psych lab and experiment Used the method of introspection
19. Philip Zimbardo Stanford Prison Experiment Social Psychology
20. Mary Ainsworth Studied attachment styles in children The type of attachment style affected the child later in life. Secure, Anxious-Ambivalent, Avoidant
21. Gordon Allport Trait Theorist
22. Solomon Asch Studied Conformity (Social Psych) Subjects were shown different lengths of lines and asked which lines matched an example line they were shown.
23. Albert Bandura Social-Cultural Perspective View Bobo Doll experiment Children learn through observational learning
24. Alfred Adler? Neo-Freudian Disagreed on Freuds view on the unconscious. Believed that we are social creatures governed by social urges and we strive for superiority
25. Alfred Binet Designed the first intelligence test.
26. Raymond Cattell Trait Theorist 16 Trait Personality Inventory
27. Noam Chomsky Linguist who developed the theory that humans are predisposed to acquire language if not learned by puberty then lose that ability.
28. Hermann Ebbinghaus Studied Memory Developed The Forgetting Curve Must rehearse
29. Paul Ekman Developmental Psychologist Pioneer of the study of emotions and their relation to facial expressions
30. Albert Ellis Cognitive Psychotherapist Founder of REBT (rational emotive behavioral therapy), you must change irrational thoughts that cause emotional problems
31. Erik Erikson Proposed that development occurs in stages. Each stage confronts a person with a new developmental task to resolve. Trust vs Mistrust Autonomy vs Shame & doubt Intiative vs guilt Industry vs inferiority Identity vs role confusion Intimacy vs isolation Generativity vs stagnation Integrity vs despair
32. Hans & Sybil Eysenck Trait theorists
33. Sigmund Freud Father of psychoanalysis Id, Ego, Superego Defense Mechanisms Our behaviors are driven by unconscious desires/motives.
34. John Garcia Studied taste aversion in rats and decided there was an evolutionary element to taste aversion
35. Howard Gardner Theorized that there are 8 different types of intellience
36. G. Stanley Hall Founded the American Journal of Psychology
37. Harry Harlow Studied attachment in baby monkeys Discovered that contact was preferred over nourishment.
38. Karen Horney Neo-Freudian Among the first to challenge Freuds bias against women. Believed that people feel anxiety because they feel isolated & helpless in a hostile world,
39. Clark Hull Developed the Drive Reduction theory
40. Carl Jung Studied under Freud, then became a Neo- Freudian People are introverts or extroverts Collective unconscious Universal archetypes
41. Lawrence Kohlberg Stage theorist that studied moral development Preconventional Conventional Postconventional
42. Elizabeth Kubler-Ross Thanatologist-one who studies death When reacting to news of impending death: 5 stages of dying Denial, anger, bargaining, depression, acceptance
43. Elizabeth Loftus Researcher on false memories
44. Konrad Lorenz Discovered the principle of imprinting
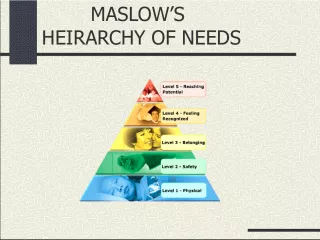
45. Abraham Maslow Humanist Hierarchy of Human Needs: Self-actualization Self-esteem Love & belonging Safety & security Physiological needs
46. William James Wrote first psych textbook: Principles of Psychology