The Nucleus: A Defining Feature of Eukaryotic Cells


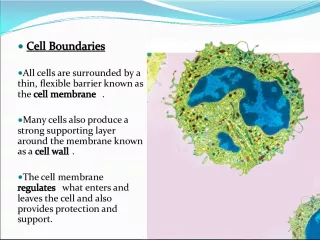
The nucleus is a distinct organelle found in both plant and animal cells that separates eukaryotic cells from prokaryotic cells. It is the largest and most easily visible organelle, housing genetic information within a double membrane. Many nuclei contain a dark staining nucleolus responsible for intense ribosomal RNA synthesis.
- Uploaded on | 0 Views
-
 tylermiller
tylermiller
About The Nucleus: A Defining Feature of Eukaryotic Cells
PowerPoint presentation about 'The Nucleus: A Defining Feature of Eukaryotic Cells'. This presentation describes the topic on The nucleus is a distinct organelle found in both plant and animal cells that separates eukaryotic cells from prokaryotic cells. It is the largest and most easily visible organelle, housing genetic information within a double membrane. Many nuclei contain a dark staining nucleolus responsible for intense ribosomal RNA synthesis.. The key topics included in this slideshow are nucleus, eukaryotic cells, plant cells, animal cells, nucleolus,. Download this presentation absolutely free.
Presentation Transcript
1. By Amanda Karzenoski & Tiffany Race
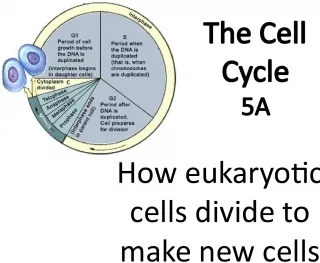
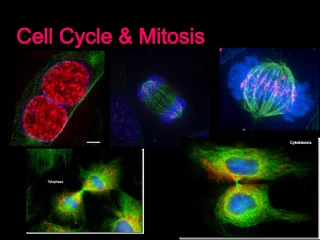
2. Found in plant and animal cells Sets Eukaryotic cells apart from prokaryotic cells Largest & most easily seen organelle Spherical structure surrounded by a double membrane Contains genetic information
4. Nucleus Many nuclei exhibit a dark staining zone called the nucleolus which is a region where intensive synthesis of ribosomal RNA is taking place.
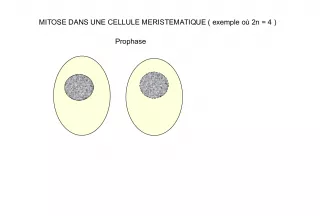
5. Nucleolus Site of genes for rRNA synthesis Synthesis of rRNA and ribosome assembly Is composed of DNA, RNA, and Protein Disappears during cell division but reappears in the final stage of mitosis
6. Questions 1. regulates the passage of molecules between the nucleus and cytoplasm A. Chromatin B. Nuclear Poles C. Ribosome's D. Protein 2. How is DNA organized in the nucleus? A. It is grouped into 4 and stored in the nucleoplasm B. It is lined up between the double layered membrane known as the nuclear envelope C. There is no specific organization, it floats freely throughout the cell until cellular division occurs D. In a complex structure called chromatin