The Elements of Chemotherapy: Understanding Drugs, Microbes, and Host


Chapter 12 delves deeper into the fundamental elements of chemotherapy, including important terminology such as bacteriostatic (which inhibits growth) and bacteric
- Uploaded on | 1 Views
-
 willieanderson
willieanderson
About The Elements of Chemotherapy: Understanding Drugs, Microbes, and Host
PowerPoint presentation about 'The Elements of Chemotherapy: Understanding Drugs, Microbes, and Host'. This presentation describes the topic on Chapter 12 delves deeper into the fundamental elements of chemotherapy, including important terminology such as bacteriostatic (which inhibits growth) and bacteric. The key topics included in this slideshow are . Download this presentation absolutely free.
Presentation Transcript
Slide1Chapter 12 Chapter 12 Drugs, Microbes, Host – The Elements of Chemotherapy Drugs, Microbes, Host – The Elements of Chemotherapy
Slide2IntroductionIntroduction Terminology Terminology Bacteriostatic (inhibits growth) vs. Bactericidal (kills organisms) Bacteriostatic (inhibits growth) vs. Bactericidal (kills organisms) Broad spectrum vs. Narrow spectrum Broad spectrum vs. Narrow spectrum Generic (chemical composition of drug) vs. Trade name (name given to a drug by a manufacture Generic (chemical composition of drug) vs. Trade name (name given to a drug by a manufacture Sources of antimicrobial agents Sources of antimicrobial agents Antibiotics - growth products of organisms Antibiotics - growth products of organisms Chemosynthetic agents - synthesized in a laboratory Chemosynthetic agents - synthesized in a laboratory Semi-synthetic agents - growth products of organisms that have been chemically altered in laboratory Semi-synthetic agents - growth products of organisms that have been chemically altered in laboratory
Slide3Colony of Streptomyces , one of nature’s most prolific antibiotic producers Colony of Streptomyces , one of nature’s most prolific antibiotic producers
Slide4Major targets of drugs acting on bacterial cells Major targets of drugs acting on bacterial cells
Slide5Mode of action of antimicrobial agents: competitive inhibition Mode of action of antimicrobial agents: competitive inhibition Antibacterial drugs Antibacterial drugs Involves inhibiting synthesis of a critical metabolite Involves inhibiting synthesis of a critical metabolite Bacteriostatic in activity Bacteriostatic in activity Examples Examples Sulfa - competition based on chemical similarity between sulfas and PABA which is needed for folic acid synthesis; folic acid critical in protein and NA synthesis; side effect = possible kidney damage from crystals Sulfa - competition based on chemical similarity between sulfas and PABA which is needed for folic acid synthesis; folic acid critical in protein and NA synthesis; side effect = possible kidney damage from crystals
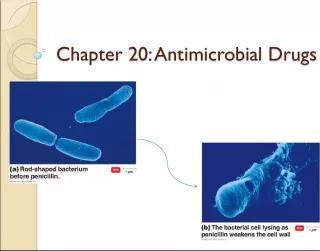
Slide6Mode of action of antimicrobial agents: inhibition of cell wall synthesis Mode of action of antimicrobial agents: inhibition of cell wall synthesis Inhibition of cell wall synthesis Inhibition of cell wall synthesis Interfere with one of multiple steps in CW synthesis Interfere with one of multiple steps in CW synthesis Greater effect demonstrated against G(+) than G(-) – most act against synthesis of peptidoglycan; many drugs cannot penetrate LPS Greater effect demonstrated against G(+) than G(-) – most act against synthesis of peptidoglycan; many drugs cannot penetrate LPS Generally considered to be bactericidal - cause lysis Generally considered to be bactericidal - cause lysis
Slide7Mode of action of antimicrobial agents: inhibition of cell wall synthesis Mode of action of antimicrobial agents: inhibition of cell wall synthesis Drugs with beta lactam ring - prevent cross-linking in last step of synthesis Drugs with beta lactam ring - prevent cross-linking in last step of synthesis Penicillins Penicillins Original penicillins effective only against G(+) - esp. staph & strep Original penicillins effective only against G(+) - esp. staph & strep Semisynthetic penicillins developed to overcome penicillinase (beta lactamase) producing strains (i.e.methicillin, oxacillin & nafcillin) and broaden spectrum to G(-) (i.e. ampicillin & carbenicillin) Semisynthetic penicillins developed to overcome penicillinase (beta lactamase) producing strains (i.e.methicillin, oxacillin & nafcillin) and broaden spectrum to G(-) (i.e. ampicillin & carbenicillin) Toxicity involves hypersensitivity Toxicity involves hypersensitivity
Slide8Mode of action of antimicrobial agents: inhibition of cell wall synthesis Mode of action of antimicrobial agents: inhibition of cell wall synthesis Cephalosporins Cephalosporins Broad spectrum antibiotics Broad spectrum antibiotics Used when individuals are allergic to penicillin Used when individuals are allergic to penicillin Modifications to original drug increased spectrum (generations 1, 2, and 3) Modifications to original drug increased spectrum (generations 1, 2, and 3) Moxalactams Moxalactams Other drugs - interfere at other steps Other drugs - interfere at other steps Cycloserine Cycloserine Bacitracin - used primarily as topical (on the skin - not taken internally because of toxicity) Bacitracin - used primarily as topical (on the skin - not taken internally because of toxicity) Vancomycin Vancomycin
Slide9Mode of action of antimicrobial agents: Inhibition of protein synthesis Mode of action of antimicrobial agents: Inhibition of protein synthesis Inhibit one of many steps in protein synthesis Inhibit one of many steps in protein synthesis Examples Examples Aminoglycosides - includes streptomycin, kanamycin, tobramycin, gentamicin, neomycin, and amikacin; causes misreading of mRNA; bactericidal; synergistic with penicillins Aminoglycosides - includes streptomycin, kanamycin, tobramycin, gentamicin, neomycin, and amikacin; causes misreading of mRNA; bactericidal; synergistic with penicillins Tetracyclines - block binding to tRNA; bacteriostatic; broad spectrum Tetracyclines - block binding to tRNA; bacteriostatic; broad spectrum Chloramphenicol - prevent peptide bond formation; bacteriostatic; excellent penetration of CNS (useful for treating meningitis); side effect = aplastic anemia Chloramphenicol - prevent peptide bond formation; bacteriostatic; excellent penetration of CNS (useful for treating meningitis); side effect = aplastic anemia Erythromycin - antimicrobial spectrum similar to penicillin; used especially in penicillin-allergic Erythromycin - antimicrobial spectrum similar to penicillin; used especially in penicillin-allergic Lincomycin and clindamycin - bacteriostatic; clindamycin useful for anaerobes; may cause pseudomembranous colitis Lincomycin and clindamycin - bacteriostatic; clindamycin useful for anaerobes; may cause pseudomembranous colitis
Slide10Structure of aminoglycoside, tetracycline, chloramphenicol, and erythromycin Structure of aminoglycoside, tetracycline, chloramphenicol, and erythromycin
Slide11Effects of drugs on bacterial cell membrane Effects of drugs on bacterial cell membrane Act directly on cell membranes (do not need to enter cell to cause damage) Act directly on cell membranes (do not need to enter cell to cause damage) Bactericidal - produce irreversible damage to membrane permeability Bactericidal - produce irreversible damage to membrane permeability Example = polymyxins and colistin Example = polymyxins and colistin Highly toxic to kidneys and nerves Highly toxic to kidneys and nerves
Slide12Antifungal drugs Antifungal drugs Damage cell membranes Damage cell membranes Bind or interfere with ergosterol (unique fungal sterol in membrane) Bind or interfere with ergosterol (unique fungal sterol in membrane) Examples Examples Polyenes - nystatin and amphotericin B Polyenes - nystatin and amphotericin B Imidazoles - clotrimazole, miconazole (topical) and ketoconazole (systemic) Imidazoles - clotrimazole, miconazole (topical) and ketoconazole (systemic) Inhibition of nucleic acid synthesis Inhibition of nucleic acid synthesis Griseofulvin - interferes with mitosis; selectively binds to keratin in skin, hair & nails; used primarily with fungi classified as dermatophytic Griseofulvin - interferes with mitosis; selectively binds to keratin in skin, hair & nails; used primarily with fungi classified as dermatophytic 5-fluorocytosine 5-fluorocytosine
Slide13Antiviral drugs Antiviral drugs Interference with uptake or uncoating of virus - amantadine (used to prevent influenza A) Interference with uptake or uncoating of virus - amantadine (used to prevent influenza A) Inhibition of nucleic acid synthesis Inhibition of nucleic acid synthesis Ribavirin - effective in vitro against a wide range of viruses; highly toxic Ribavirin - effective in vitro against a wide range of viruses; highly toxic Acyclovir - Herpes-specific (genital herpes, cold sores, chickenpox) Acyclovir - Herpes-specific (genital herpes, cold sores, chickenpox) Azidothymidine (AZT) - treatment of HIV infections Azidothymidine (AZT) - treatment of HIV infections
Slide15Antibiotic resistance in bacteria Antibiotic resistance in bacteria Sites of resistance Sites of resistance Membrane transport - LPS layer of G(-) prevent entry of many drugs Membrane transport - LPS layer of G(-) prevent entry of many drugs Targets of antimicrobial agents (e.g. ribosomes) Targets of antimicrobial agents (e.g. ribosomes) Presence of antibiotic- destroying enzymes (e.g. beta lactamase) Presence of antibiotic- destroying enzymes (e.g. beta lactamase)
Slide16Antibiotic resistance in bacteria Antibiotic resistance in bacteria Mechanisms of changing resistance Mechanisms of changing resistance Mutations - permanent changes in chromosomes; not caused by antibiotics Mutations - permanent changes in chromosomes; not caused by antibiotics Acquisition of new genetic information - methods Acquisition of new genetic information - methods Transformation = naked DNA Transformation = naked DNA Transduction = via viruses Transduction = via viruses Conjugation = via sex pili (sexual recombination) – most rapid method Conjugation = via sex pili (sexual recombination) – most rapid method Selective pressures of antimicrobial therapy - use of antibiotics select for bacteria that are resistant - sensitive bacteria are destroyed Selective pressures of antimicrobial therapy - use of antibiotics select for bacteria that are resistant - sensitive bacteria are destroyed
Slide17Antibiotic susceptibility testing Antibiotic susceptibility testing Susceptibility no longer predictable Susceptibility no longer predictable Variables affecting outcome of therapy Variables affecting outcome of therapy Condition of host (immune status - underlying diseases) Condition of host (immune status - underlying diseases) Site of infection (can drugs get to site?) Site of infection (can drugs get to site?) Properties of antimicrobial agent Properties of antimicrobial agent Other drugs taken concurrently Other drugs taken concurrently Susceptibility of organism to drug Susceptibility of organism to drug
Slide18The role of antimicrobials in disrupting microbial flora and causing superinfections The role of antimicrobials in disrupting microbial flora and causing superinfections
Slide19Broth dilution methods (Minimal Inhibitory Concentration) – Quantitative Method Broth dilution methods (Minimal Inhibitory Concentration) – Quantitative Method Procedure Procedure Uses decreasing concentrations of antimicrobial agents prepared in 2-fold dilutions of broth that will support growth of test organism Uses decreasing concentrations of antimicrobial agents prepared in 2-fold dilutions of broth that will support growth of test organism Standard inoculum is added to broth containing dilutions of antimicrobial agent, incubated overnight and then examined for growth (turbidity) Standard inoculum is added to broth containing dilutions of antimicrobial agent, incubated overnight and then examined for growth (turbidity) Lowest concentration of agent that inhibits growth as detected by lack of visible turbidity = Minimal Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) Lowest concentration of agent that inhibits growth as detected by lack of visible turbidity = Minimal Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) Susceptibility and resistance determined by break point of drug (highest conc. of drug in the blood that can be achieved with maximal therapy); if MIC is lower than breakpoint, organism = susceptible; if MIC is higher than breakpoint, organism = resistant Susceptibility and resistance determined by break point of drug (highest conc. of drug in the blood that can be achieved with maximal therapy); if MIC is lower than breakpoint, organism = susceptible; if MIC is higher than breakpoint, organism = resistant
Slide20Minimum Inhibitory Concentration Minimum Inhibitory Concentration
Slide21Disk diffusion (Kirby/Bauer) - Qualitative Disk diffusion (Kirby/Bauer) - Qualitative Advantage - rapid testing of several antibiotics simultaneously Advantage - rapid testing of several antibiotics simultaneously Uses antimicrobial agents incorporated into filter paper disks placed on agar media causing drug to diffuse creating a concentration gradient (conc. highest closest to disk) Uses antimicrobial agents incorporated into filter paper disks placed on agar media causing drug to diffuse creating a concentration gradient (conc. highest closest to disk) Susceptibility/resistance determined by measuring diameter of zone of inhibition around disk and comparing to established zones for each antibiotic Susceptibility/resistance determined by measuring diameter of zone of inhibition around disk and comparing to established zones for each antibiotic Standardization - Bauer, Kirby, Sherris & Turck (correlated with MIC’s using large numbers strains & regression analysis) Standardization - Bauer, Kirby, Sherris & Turck (correlated with MIC’s using large numbers strains & regression analysis)
Slide22Techniques for preparation and interpretation of disc diffusion tests Techniques for preparation and interpretation of disc diffusion tests
Slide23Antimicrobial gradient strip method (E test) Antimicrobial gradient strip method (E test) Disk diffusion method that allows determination of MIC in agar Disk diffusion method that allows determination of MIC in agar Consists of plastic strip containing gradient of antimicrobial agent along with an interpretive scale Consists of plastic strip containing gradient of antimicrobial agent along with an interpretive scale Performed similar to disk diffusion Performed similar to disk diffusion Organisms grow in elliptical zone of inhibition around strip relative to concentration of antibiotic along its length Organisms grow in elliptical zone of inhibition around strip relative to concentration of antibiotic along its length MIC determined by reading scale at point where zone of inhibition intersects strip MIC determined by reading scale at point where zone of inhibition intersects strip