Understanding Digestive System: Its Functions and Types of Digestion

The digestive system is responsible for breaking down food into small molecules, which are then absorbed through the blood to provide energy. There are two types of digestion: mechanical and chemical. Mechanical digestion involves cutting, mixing, or churning food into smaller pieces, while chemical digestion relies on saliva, bile, and acid to break down food molecules.
- Uploaded on | 5 Views
-
 kinslee
kinslee
About Understanding Digestive System: Its Functions and Types of Digestion
PowerPoint presentation about 'Understanding Digestive System: Its Functions and Types of Digestion'. This presentation describes the topic on The digestive system is responsible for breaking down food into small molecules, which are then absorbed through the blood to provide energy. There are two types of digestion: mechanical and chemical. Mechanical digestion involves cutting, mixing, or churning food into smaller pieces, while chemical digestion relies on saliva, bile, and acid to break down food molecules.. The key topics included in this slideshow are Digestive system, Functions, Types of digestion, Mechanical digestion, Chemical digestion,. Download this presentation absolutely free.
Presentation Transcript
1. Digestive System
2. 1 Function: Break down food into small molecules so it can be absorbed and moved by the blood which delivers it to your cells for energy.
3. 2 Types of digestion
4. 2 types of digestion Mechanical: food is cut, mixed, or churned into smaller pieces.
5. 2 types of digestion Chemical: saliva, bile, and acid help break down or dissolve the chemical bonds of the food molecules
6. The Path of Food 1. Ingestion (eating) 2. Digestion (breaking down food molecules) 3. Absorption (by cells) 4. Elimination (disposal of unused food)
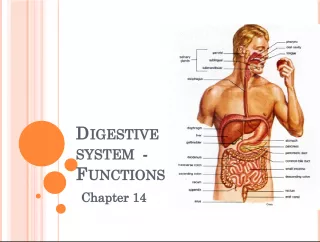
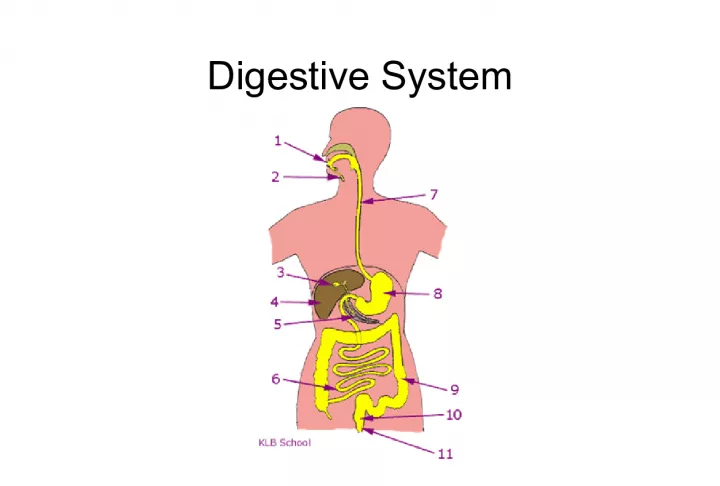
7. Organs of the Digestive System
8. 1. Food is chewed in the mouth Mechanical-chewing and ripping it into smaller pieces Chemical-saliva starts to dissolve starches http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CsYbO6zBR74
9. 2. Slimy pieces of food slide down the pharynx, past the epiglottis, into the esophagus http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QvGYvK6qScE&feature=related
10. 3. Food is squeezed down the esophagus by muscle contractions called peristalsis .
11. 4. Food lands in the stomach Mechanical digestion-food is churned and mixed Chemical digestion-food is mixed with enzymes and acids to break it down. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=cp-SEs6dxR8&feature=related heartburn video
12. 5. 2-4 hours later, food is now a watery liquid and it slowly moves into your small intestine .
13. Stomach Stapling Stomach size is reduced and intestinal length is shorted to reduce the amount of food stored and calories absorbed. This reduces the size of the stomach and small intestine, thereby restricting food intake and caloric absorption.
14. Small Intestine 6. In the small intestine food is digested even more and then absorbed by the bloodstream.
15. 7. Fat is chemically digested in the small intestine by bile. The liver makes bile and extra bile is stored in the gall bladder
16. Carbohydrates, proteins, and fats are also chemically digested by a digestive solution made by the pancreas .
17. 8. Millions of villi in the small intestine allow the blood to pick up the nutrients (absorb) to deliver to cells around the body. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xu5jDCX2cHM http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_GTQBiZni6w
18. 9. Remaining food and liquid is moved into your large intestine by peristalsis.
19. 10. Water is absorbed from the large intestine back into the body. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PpzfKt-47iA&feature=related
20. 11. Remaining food is compacted and released from the body as feces through the rectum and anus.
21. The End!
22. 1. Mouth 2. Salivary Glands 3. Gall Bladder 4. Liver 5. Pancreas 6. Small Intestine 7. Esophagus 8. Stomach 9. Large Intestine 10. Rectum 11. Anus
23. Review of digestion 1. Draw a plate of food
24. a. Mechanical digestion by teeth (tear dinner in half) b. Chemical digestion by saliva (tear dinner in half again) 2. Food goes into the mouth
25. 3. Food moves into the esophagus No digestion occurs
26. 4. Into the stomach a. Mechanical digestion churning muscles (tear pieces in half) b. Chemical digestion by acid (tear pieces in half again)
27. 5. Into the small intestine a. Chemical digestion by bile (tear pieces in half again) b. Absorption by blood stream (I will come around and collect some nutrients)
28. 6. Into the large intestine a. Absorption of water by blood stream (I will come around and collect some water)
29. 7. Elimination of unused food a. Form compact feces from remaining food particles (I will come around and collect the feces)