Introduction to Echinoderms and Embryological Differences

In this lab, students will learn about the characteristics of the Echinodermata phylum and understand the differences between protostomes and deuterostomes. They will observe the early stages of embryo development using starfish embryo slides and examine the external and internal features of starfish.
- Uploaded on | 4 Views
-
 alessandro
alessandro
About Introduction to Echinoderms and Embryological Differences
PowerPoint presentation about 'Introduction to Echinoderms and Embryological Differences'. This presentation describes the topic on In this lab, students will learn about the characteristics of the Echinodermata phylum and understand the differences between protostomes and deuterostomes. They will observe the early stages of embryo development using starfish embryo slides and examine the external and internal features of starfish.. The key topics included in this slideshow are Echinoderms, protostomes, deuterostomes, embryo development, starfish,. Download this presentation absolutely free.
Presentation Transcript
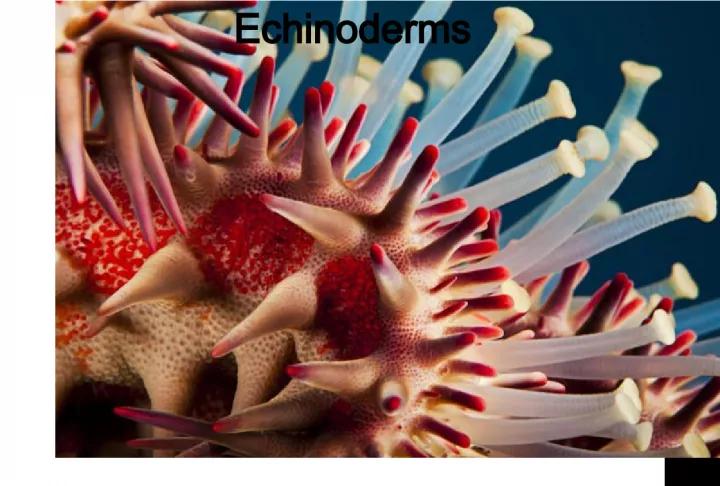
1. Echinoderms
2. Goals of the lab: to introduce general characteristics of the phylum Echinodermata to understand the embryological differences between protostomes and deuterostomes to observe initial stages of embryo development, using prepared slides of starfish embryos to examine external and internal features of the starfish, as a representative of the phylum Echinodermata Echinoderms
3. Phylum Echinodermata eumetazoan (true tissues) bilaterally symmetrical larvae; radially symmetrical adults eucoelomate deuterostome
4. Phylum Echinodermata Class Astroidae Class Ophiuroidae Class Echinoidae Class Holothuroidae Class Crinoidae Sea stars Brittle stars Crinoids Sea urchins Sea cucumbers
5. Phylum Echinodermata No circulatory system No respiratory system Excretion (N elimination) by diffusion Simple nervous system, no brain Water-vascular system
6. A Comparison of Early Development in Protostomes and Deuterostomes
7. Early Embryonic Development
8. Unfertilized egg Starfish Development 2 blastomeres After fertilization & 1st cleavage 4 blastomeres 2nd cleavage 8 blastomeres 3rd cleavage 16 blastomeres 4th cleavage 32 blastomeres 6th cleavag e, next slide 5th cleavage
9. Starfish Development (continued) 64 blastomeres Non-motile blastula Ciliated blastula * blastula is same size as unfertilized egg Gastrula: Beginning invagination blastopore Gastrula: During invagination Gastrula: Archenteron, no mesenchyme Next slide
10. Starfish Development (continued) Gastrula: Archenteron with mesenchyme Late gastrula: lateral view Early bipinnaria larva, lateral view Brachiolaria larva Young starfish Late bipinnaria larva, lateral view blastopore becomes anus 2nd opening becomes mouth
11. Sea urchin larvae: pluteus Starfish larvae: Bipinnaria Sea cucumber & Crinoid: doliolaria larvae Brittle star larvae: pluteus
12. Phylum Echinodermata Tube feet & associated plumbing Used for walking, clinging to substrate & holding food Water Vascular System
13. Starfish water vascular system
14. Class Echinoidea: sea urchins Echinometra mathaei Collector urchin Echinothrix calamaris
15. Class Echinoidea: sea urchins Diadema
16. Class Echinoidea: sea urchins Slate pencil urchin
17. Colobocentrotus atratus Class Echinoidea: sea urchins
18. Class Holothuroidea: Sea Cucumbers Holothuria atra Polyplectana kerfersteninii
19. Class Holothuroidea: Sea Cucumbers http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Fw2DrbhOA-M Pearlfish in seacucumber
20. Linckia sp. Class Asteroidea: Sea Stars Pin cushion
21. Class Asteroidea: Sea Stars http://www.arkive.org/crown-of-thorns- starfish/acanthaster-planci/video-00.html
22. Class Ophiuroidea: Brittle Stars Ophiocoma erinaceus
23. Class Crinoidea: Feather Stars
24. Starfish Dissection: Schematic View
25. Starfish: Oral View Mouth Ambulacral groove Spines Tube feet
26. Starfish Dissection: Skeleton Removed: Aboral View Stone canal Digestive glands Gonads Pyloric stomach Cardiac stomach
27. Starfish Arm: Digestive Glands Removed Ambulacral Plates Ampullae Cardiac Stomach Gonads