Comparing the Three Colonial Regions in American History


This article explores the similarities and differences among the three colonial regions in America, each with distinct economic, social, and political characteristics, despite all being expected to supply raw materials and purchase finished goods from England.
- Uploaded on | 1 Views
-
 mayaroy
mayaroy
About Comparing the Three Colonial Regions in American History
PowerPoint presentation about 'Comparing the Three Colonial Regions in American History'. This presentation describes the topic on This article explores the similarities and differences among the three colonial regions in America, each with distinct economic, social, and political characteristics, despite all being expected to supply raw materials and purchase finished goods from England.. The key topics included in this slideshow are . Download this presentation absolutely free.
Presentation Transcript
1. The 13 Colonies in American History What were the similarities and differences among the three colonial regions? Let’s Begin!
2. Regional Differences Among American Colonies All colonies were expected to provide England with raw materials & purchase finished products from England, however, by the late 1600’s, England’s American colonies were developing along three regional patterns. Each region had distinct economic, social, and political characteristics.
3. The First Colonies • Jamestown was the first colony established in 1607 in what is now Virginia. • John Smith was sent by the Virginia Trading Company to start a trading post. • Here the settlers learned about tobacco. • Tobacco became Jamestown’s “black gold”. Home
4. The First Colonies Cont. • In 1620, the founded Plymouth Colony. Plymouth Colony was in what we know as Cape Cod. • The pilgrims left England because they wanted religious freedom from the King. • When the Pilgrims left England they had agreed to work for the Virginia Trading Company by sending back furs, fish and lumber. P i l g r i m s A person who makes a journey for a religious reason. Continue Home
5. New England Colonies • Included these states: – Rhode Island – Connecticut – Massachusetts – New Hampshire • Most New England colonies were founded for religious reasons, so the ability to read the bible was important. Continue Home
6. New England Colonies • All but one of the New England colonies had school laws in place by 1671. • New Englanders were almost exclusively of English background.
7. New England Colonies • Products: – Whaling – Fishing – Shipbuilding – Furs – Lumber • Colonists here grew their own food and made most of what they needed. They were very self-sufficient. Continue Home
8. New England Colonies • Agriculture was limited by the cold climate so farms were small with little demand for slaves. • Colonists settled close to each other in towns & the New England region became the most urbanized region. Continue Home
9. The Middle Colonies • The Middle Atlantic colonies were the most diverse in terms of people, religion, and economy. • Colonists primarily of English background, but included Dutch, German, & Scots-Irish. • Turn to your partner and discuss how diversity in natural resources and population could lead to the development of large cities. Continue
10. The Middle Colonies As a result of diverse natural resources (iron ore, fertile soil, temperate climate), a combination of rural farm areas, small towns, & cities developed. N.Y. & Philadelphia are the two largest cities in the colonies. Continue Home
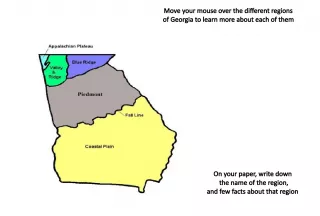
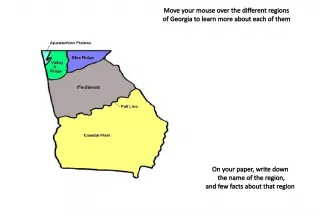
11. The Southern Colonies • Included these states: – Maryland – North Carolina – South Carolina – Virginia – Georgia Continue Home
12. Southern Colonies • Cash crops included: – Tobacco – Rice – Indigo – plant used to make dyes • Plantation agriculture depended on cheap labor. Continue Home
13. Slave Trade • As demand for slaves increased, traders in both England and America hoped to make a profit. • The “Triangular Trade” http://www.eduplace.com/kids/socsci/books/app lications/imaps/maps/g5s_u3/index.html#top Continue Home
14. Southern Colonies • There were few towns in the southern colonies, but several times a year families living on plantations would travel to the county seat . This was the main town for each county, or large part of a colony. • People went to church and traded crops for goods at the county seat. • County seats had a courthouse, church, general store, and a jail • Plantation owners bought and sold slaves here. Continue Home
15. Life on the Plantations • Planters bought as much land as they could in order to grow more cash crops. These areas of land were known as plantations . • Plantations were usually built along waterways. The river was used to transport crops to market. Continue Home
16. Plantation Diagram Why do you think plantations were built near waterways? Continue
17. Life on the Plantations • Indentured servants worked on plantations. This was a person who agreed to work for another person without pay for a certain length of time. This was often from 4-7 years. Once their time was over, the indentured servant was free. • Some indentured servants had not agreed to work on plantations. Some were kidnapped and sold in the colonies. Many traders were bringing Africans to the colonies as slaves. Unlike indentured servants, slaves were not given their freedom and were slaves for life. Continue Home
18. Interactive Quiz • History Alive! Tutorial .