Plant Structure and Growth: Investigation 2 - Vascular Plants


In this 5th grade investigation, students will explore the structure and growth of vascular plants. The accompanying video notes provide an overview of the key concepts, including the
- Uploaded on | 3 Views
-
 albertofletcher
albertofletcher
About Plant Structure and Growth: Investigation 2 - Vascular Plants
PowerPoint presentation about 'Plant Structure and Growth: Investigation 2 - Vascular Plants'. This presentation describes the topic on In this 5th grade investigation, students will explore the structure and growth of vascular plants. The accompanying video notes provide an overview of the key concepts, including the. The key topics included in this slideshow are . Download this presentation absolutely free.
Presentation Transcript
Slide1Plant Structure and Growth Plant Structure and Growth 5th Grade 5th Grade Investigation 2 “Vascular Plants” Investigation 2 “Vascular Plants” Video Notes Video Notes
Slide2Question 1 Question 1 What do all plants have in common? What do all plants have in common?
Slide3Question 1 Answer Question 1 Answer All plants are multicelled, have rigid cell walls, usually contain chlorophyll, have tissues and organs. All plants are multicelled, have rigid cell walls, usually contain chlorophyll, have tissues and organs.
Slide4Question 2 Question 2 What are the two types of vascular plant tissue that make up the vascular bundle? What are the two types of vascular plant tissue that make up the vascular bundle?
Slide5Question 2 Answer Question 2 Answer The two types of vascular plant tissue that make up the vascular bundle are xylem and phloem . The two types of vascular plant tissue that make up the vascular bundle are xylem and phloem .
Slide6Question 3 Question 3 Compare the roles of xylem and phloem. Compare the roles of xylem and phloem.
Slide7Question 3 Answer Question 3 Answer Xylem transports water and nutrients from the roots up to the other parts of the plant. Phloem transports sugar from the leaves to all of the other parts of the plant. Xylem transports water and nutrients from the roots up to the other parts of the plant. Phloem transports sugar from the leaves to all of the other parts of the plant.
Slide8Question 4 Question 4 How are the trunk of a tree and a stem of a flowering plant the same? How are the trunk of a tree and a stem of a flowering plant the same?
Slide9Question 4 Answer Question 4 Answer The trunk of the tree and a stem of a flowering plant are both made up of vascular bundles that transport water, nutrients, and sugar to different parts of the plant. The trunk of the tree and a stem of a flowering plant are both made up of vascular bundles that transport water, nutrients, and sugar to different parts of the plant.
Slide10Question 5 Question 5 How do the rings in a tree trunk form? How do the rings in a tree trunk form?
Slide11Question 5 Answer Question 5 Answer As the tree grows, it produces new vascular tissue. The oldest tissue is in the center of the stem, and the newest living tissue is in the outer part of the trunk. As the tree grows, it produces new vascular tissue. The oldest tissue is in the center of the stem, and the newest living tissue is in the outer part of the trunk.
Slide12Question 6 Question 6 When you look at a cross section of a tree trunk, why are some trunk rings narrow and others wide? What does that tell you about the tree? When you look at a cross section of a tree trunk, why are some trunk rings narrow and others wide? What does that tell you about the tree?
Slide13Question 6 Answer Question 6 Answer Wide rings of a tree trunk are laid down during very wet years when the tree produces lots of xylem cells to transport the water from the roots to the rest of the plant and then transpire through the stomata. Wide rings of a tree trunk are laid down during very wet years when the tree produces lots of xylem cells to transport the water from the roots to the rest of the plant and then transpire through the stomata. During a dry year , the tree doesn’t grow many xylem cells, so the ring is narrow. During a dry year , the tree doesn’t grow many xylem cells, so the ring is narrow.
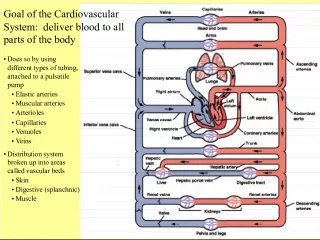
Slide14Question 7 Question 7 How is the vascular system of plants like the circulatory system of humans? How is the vascular system of plants like the circulatory system of humans?
Slide15Question 7 Answer Question 7 Answer Vascular Plants Vascular Plants Human Human Both plants and people have specialized structures for Both plants and people have specialized structures for transport nutrients to cells. transport nutrients to cells. One-way transportation system for water & minerals (up) and a second one-way system for sugar (down.) One-way transportation system for water & minerals (up) and a second one-way system for sugar (down.) Have a Circulatory System with blood that goes around the human body. Have a Circulatory System with blood that goes around the human body. Plants have a xylem and a phloem. Plants have a xylem and a phloem. Arteries, capillaries, and veins for transportation of nutrients Arteries, capillaries, and veins for transportation of nutrients