The Arab-Israeli Conflict: Sykes-Picot Agreement (1916) & Balfour Declaration (1917)

The Sykes-Picot Agreement was a secret agreement between France and Britain in 1916 that defined the spheres
- Uploaded on | 2 Views
-
 stephanie666
stephanie666
About The Arab-Israeli Conflict: Sykes-Picot Agreement (1916) & Balfour Declaration (1917)
PowerPoint presentation about 'The Arab-Israeli Conflict: Sykes-Picot Agreement (1916) & Balfour Declaration (1917)'. This presentation describes the topic on The Sykes-Picot Agreement was a secret agreement between France and Britain in 1916 that defined the spheres. The key topics included in this slideshow are . Download this presentation absolutely free.
Presentation Transcript
Slide1Arab-Israeli Conflict
Slide2Sykes-Picot Agreement 1916• Secret Agreement between France & Britain • Defined the spheres of influence that France & Britain would have over Ottoman land after WWI
Slide3The Balfour DeclarationForeign Office November 2nd, 1917 Dear Lord Rothschild: I have much pleasure in conveying to you on behalf of His Majesty's Government, the following declaration of sympathy with Jewish Zionist aspirations which has been submitted to, and approved by, the Cabinet: His Majesty's Government view with favor the establishment in Palestine of a national home for the Jewish people, and will use their best endeavors to facilitate the achievement of this object, it being clearly understood that nothing shall be done which may prejudice the civil and religious rights of existing non-Jewish communities in Palestine, or the rights and political status enjoyed by Jews in any other country. I should be grateful if you would bring this declaration to the knowledge of the Zionist Federation. Yours, Arthur James Balfour
Slide4Post–WWI Reality
Slide5Inter-War Period• Arabs felt betrayed by the West after promised & denied independence • Balfour Declaration led to a commitment by Britain to a national homeland for Jews in Palestine (but the Palestinians were there) and furthered the Zionist movement begun in the late 19 th century • At first, Arabs welcomed economic boost, but when Jews began to clear the land of Arab tenants & refused to hire Palestinian workers conflict
Slide6Post-WWII• After the holocaust, Jewish migration to Israel, conflict w/ Palestinians & world-wide sympathy led to Britain referring the Palestinian issue it created to the U.N. • 1947 – U.N. called for a partition of Palestine w/ Jerusalem as an international city (Jews got 55% land while only 34% of the population) Palestine & Islamic countries voted against, but Jews voted for • May 14, 1948 – Israel independent w/ David Ben Gurion as P.M.
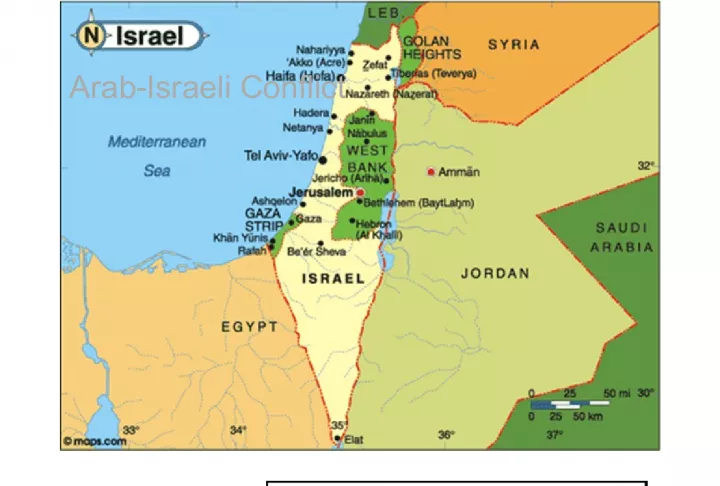
Slide81948-1949The day after independence, Egypt, Iraq, Jordan, Lebanon, Saudi Arabia & Syria invaded Israel • Israel seized ½ Palestinian land • Egypt Gaza Strip • Jordan West Bank • Palestinians no land (refugees)
Slide101956 Suez Crisis1956 Suez Crisis Gamal Abdel Nasser, Egyptian President, nationalized the Suez Canal Britain, France & Israel invaded Egypt & took the Canal • Pressure by U.S. & U.S.S.R. forced Israel to withdraw Egypt in charge of Canal
Slide111967 Six-Day WarNasser moved to close off the Gulf of Aqaba Israel attacked Egypt, Iran, Jordan & Syria • Israel Sinai Peninsula (incl. Gaza Strip), Golan Heights, West Bank & Old Jerusalem
Slide12After the 1973 War1973 Anwar Sadat (Nasser’s successor) led surprise Arab attack on Yom Kippur & Golda Meir (Israeli P.M.) launched counterattack – truce signed, but no peace treaty
Slide13PE A C E ? November 1977 In Jerusalem, Sadat offered peace to Israel in exchange for withdrawal from 1967 War territories & recognize Palestinians’ rights • 1978 U.S. Pres. Carter invited Sadat & Menachem Begin (Israeli P.M.) to Camp David • 1979 Camp David Accords • World praised Sadat, but Muslim extremists assassinated him 1981 • 1982 Israel withdrew from Sinai 1970s & 1980s Palestinian Liberation Organization (PLO) formed under Yasir Arafat Campaign of civil disobedience (intifada) influenced world opinion • October 1991, Israeli & Palestinian delegates met for the first time in peace talks 1993 Declaration of Principles (peace talks at Oslo, Norway) • Yitzak Rabin (Israeli P.M.) agreed to give Palestinians self-rule in the Gaza Strip & West Bank • 1993 Rabin & Arafat signed at the White House in D.C. • 1995 Rabin assassinated
Slide15Israeli Settlements
Slide16Will Recent Events Lead to Peace?• 2000 - negotiations for a final settlement (at Camp David) ended in deadlock – each side blaming the other • 2 nd Intifada - violence resumed after Ariel Sharon (then General) visited the temple mount • 2002 – Saudi proposal for peace was adopted by the Arab League & became a U.N. Resolution (1 st time Arab countries called for a Palestine alongside Israel) – Israel rejected it • Suicide bombings & resultant Israeli occupation continues to hinder peace
Slide18Israel’s Security Barrier(a.k.a. “Security Fence” or “Apartheid Wall”)
Slide22Recent Event Peace? (cont.) • 2004 – Syria tried to renew peace treaty talks w/ Israel from 1967, but has met cool reception • November 11, 2004 - Yasser Arafat died Mahmoud Abbas became Palestinian leader • 2005 – Sharm El Sheikh Conference – both sides agreed to end violence & Israel’s Knesset approved Disengagement Plan (withdrawal of 24 settlements) • Nevertheless violence continued • 2006 – Hamas (organization w/ terrorist ties) won election in Palestinian legislature (Abbas still President) • 2012 – the State of Palestine replaced the PLO in the UN & upgraded its status as “non-member observer” • Egypt is leading cease-fire efforts re: current flare-ups