Understanding the Nervous System
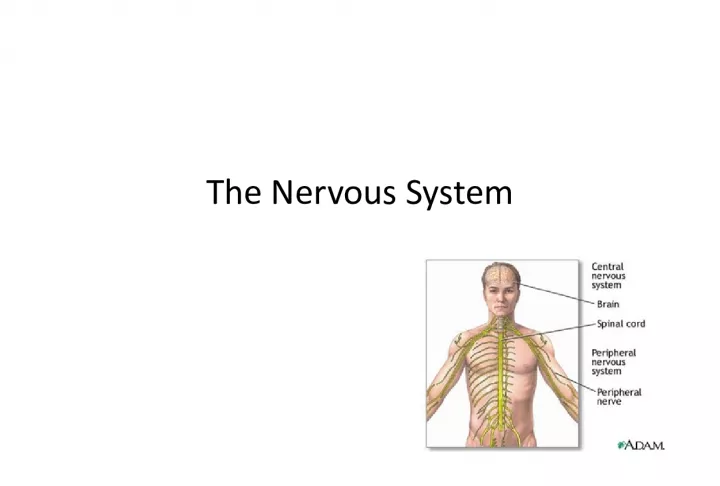

The nervous system comprises the brain, spinal cord, and nerves. Neurons send signals while glial cells protect and support them. Sensory neurons monitor stimuli, while motor neurons carry impulses to muscles and glands.
- Uploaded on | 5 Views
-
 abhishekbangera
abhishekbangera
About Understanding the Nervous System
PowerPoint presentation about 'Understanding the Nervous System'. This presentation describes the topic on The nervous system comprises the brain, spinal cord, and nerves. Neurons send signals while glial cells protect and support them. Sensory neurons monitor stimuli, while motor neurons carry impulses to muscles and glands.. The key topics included in this slideshow are . Download this presentation absolutely free.
Presentation Transcript
1. The Nervous System
2. Review: What makes up the Nervous System? The brain Spinal cord Nerves 2 types of cells: neurons: send and receive signals glial cells: protect, support, and insulate neurons
4. Review: What are the two types of neurons? Sensory neurons What do sensory neurons do? Cells that monitor stimuli and send signals to the spinal cord or brain. Motor neurons What do motor neurons do? Cells that carry impulses from the brain or spinal cord to muscles, glands, or other neurons
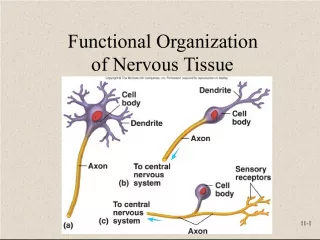
5. Lets take a closer look at a neuron. Dendrites -branchlike structures on the cell body that receive the signal Cell body -Central part of the neuron that contains the cell nucleus Axon -rod-like extension off of cell body which conducts signal through neuron On your diagram, label dendrite, cell body, cell nucleus, and axon.
6. A Neuron Glial cell
7. How are neurons organized? Each neuron connects to 100s of thousands of other neurons.
8. How is a signal sent? First, a stimulus happens. A stimulus is any incoming information that causes a response. The signal moves from the stimulus dendrites cell body axon another neuron. Sensory neurons detect the stimulus, and begin to send an electrical signal that passes through several neurons. The signal then starts all over in another neuron.
10. Is it that easy? No. When the signal gets to the end of a neuron, it comes to a synapse , or a small space between the neurons.
11. What happens at the synapse? In order to transmit the signal from one neuron to another across the synapse, the neuron releases a chemical called a neurotransmitter. Neurotransmitters act as chemical messengers from one neuron to another.
13. Neurotransmitters and Disease Dopamine is a neurotransmitter related to muscular function Serotonin is a neurotransmitter that is associated with happy nerve signals
14. Once a signal is sent through the neurons, where does it go? It is usually sent to the brain, processed, and then another signal is sent through the motor neurons to induce movement or give a response.
15. Think about when you touch a hot object. You withdraw your hand without having to think at all. Your brain processes it later. This quick response to a stimulus that does not require a trip to the brain is called a reflex arc.
16. The brain is not involved in a reflex arc. Look at the picture describe where the signal is sent and how it is returned.
17. Ms. Pleckis Biology Class Proudly Presents.
18. Study your notes for 3 minutes.
19. Motor Neurons Left hand= dendrite Body= cell body Right hand= axon
20. http://teachhealthk- 12.uthscsa.edu/curriculum/brain/pa03pdf/03 01E-Wires.pdf