Reviewing the Impact of European Exploration and Colonization in the VA US SOLs


This review delves into the significance of SOLs 2 and 3, which focus on Exploration and Colonization in the VA US curriculum.
- Uploaded on | 2 Views
-
 oskold
oskold
About Reviewing the Impact of European Exploration and Colonization in the VA US SOLs
PowerPoint presentation about 'Reviewing the Impact of European Exploration and Colonization in the VA US SOLs'. This presentation describes the topic on This review delves into the significance of SOLs 2 and 3, which focus on Exploration and Colonization in the VA US curriculum.. The key topics included in this slideshow are . Download this presentation absolutely free.
Presentation Transcript
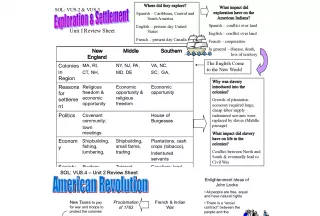
Slide1VA/US SOL Review of Unit 1:SOLs 2- 3 Exploration & Colonization
Slide2European Exploration & Colonization• Resulted in a redistribution of the world population (voluntarily & involuntarily)
Slide3Exploration & Colonization…• Initiated worldwide commercial expansion due to Columbian Exchange of agricultural products. • Colonization also led to new ideas about representative government & religious tolerance .
Slide4Columbian Exchange
Slide5America• Already populated by Native Americans (Indians) • Seen as “Savages” by Europeans
Slide6Exploration & Colonization• Exploration & settlement of the English in America & the Spanish in the Caribbean, Central & South America, often led to violent conflicts with the Indians. • Yet, French exploration in Canada didn’t. – Why not? • Indians lost traditional territories & died from diseases .
Slide7Different ColoniesNew England • Use of town meetings (like Athens ) as a form of direct democracy Southern Colonies • Maintained stronger ties w/ England, but had representative colonial legislatures Middle Colonies Incorporated a number of democratic principles that were similar to Englishmen
Slide8Slavery/ Indentured Servitude• The first Africans were brought against their will in 1619 . • The African slave trade resulted from labor shortages. • Slaves were brought over on the Middle Passage • Some indentured servants had worked before slaves. Not many more came after slavery became prominent. • Slavery eventually led to the Civil War .
Slide913 Original Colonies• New England • Middle Colonies • Southern Colonies
Slide10New England Colonies• Mainly settled by Puritans seeking religious freedom • Also settled by Pilgrims • Sought economic opportunities • Direct-democracy (town meetings) • Covenant Community – God-like – Mayflower Compact & Puritan religious beliefs • Intolerant of Non-Puritans
Slide11New England Colonies…• Economy – Shipbuilding, Fishing , Lumbering, Subsistence farming & (eventually) manufacturing – Valued hard work & thrift • Society – Family centered – Religious Standing – Intolerant of dissenters
Slide12New England Colonies…• Society… – Intolerant • Rhode Island: Roger Williams • Anne Hutchinson • Politics – Church leaders • Mix Church & State – Male-dominated – Town Meetings
Slide13Middle Colonies• Settled mainly by English, Dutch & German- speaking immigrants – NY used to be New Netherlands • Wanted religious freedom & economic opportunity • Most diverse population
Slide14Middle Colonies…• Economy – Shipbuilding , Small-scale farming & Trading • Skilled artisans • NYC & Philly became commercial centers • Society – Home to multiple religious groups who believed in religious tolerance • Quakers (PA), Huguenots & Jews (NY), Catholics (MD), Presbyterians (NJ) – Flexible social structures – Middle -class of artisans, entrepreneurs & farmers
Slide15Middle Colonies…• Political – Incorporated a number of democratic principles that reflected the basic rights of Englishmen – Did not mix Church & State/ Tolerant of other religions
Slide16Southern Colonies• Mainly settled by the English Cavaliers & poorer English & Scots-Irish – Cavaliers = English nobility who received large land grants in eastern VA from the King – Indentured Servants, Debtors, Prisoners – African slaves • Wanted economic opportunities – Jamestown was a business venture established by the VA Company of London
Slide17Jamestown• 1 st Permanent English Settlement, established by the VA Company of London in 1607 • In the middle of Powhatan Nation • 1 st settlers were mainly Gentlemen – “Don’t Work = Don’t Eat!” was John Smith’s rule • Headright System • “Starving Time” due to weather • John Rolfe planted tobacco & married Pocahontas
Slide18Southern Colonies…• Economy – Large plantations in the coastal lowlands grew “cash crops:” Indigo , Rice, Tobacco – Western foothills & mountains they had small-scale subsistence farming, hunting & trading • Society – Based on family status & ownership of land – Large landowners dominated colonial government – Closer ties to England & the Church of England than other colonies – Western VA had a lot of S cots-Irish & English men
Slide19Southern Colonies…• Political – Maintained stronger ties with Britain – Large landowners dominated colonial legislatures – VA House of Burgesses • 1 st Elected Legislature in the New World • Representative Democracy • Today it’s known as the VA General Assembly
Slide20Indentured Servitude & Slavery• Indentured Servant = Someone who works for 4-7 years in exchange for passage over to the New World. – Headright system = promise of land • Growth of southern plantation-economy required cheap labor in large numbers. Originally met by indentured servants.
Slide21Indentured Servitude & Slavery…• Most tobacco plantation needs eventually were filled by importation of Africans. – Some were indentured servants & free – Middle Passage – Slave Codes = laws that limited what slaves could do • Development of slavery-based economy eventually led to Civil War.
Slide22Question Time!!!Show me what you know
Slide23 establishment of early american Colonies Roanoke Massachusetts 1587 1620 /--------/--------/-----------/ 1565 1607 St. Augustine Jamestown 1. Which date on this timeline represents the beginning of a permanent British presence in North America? A. 1565 B. 1587 C. 1607 D. 1620
Slide242. Which colony was established as a businessventure? A. Connecticut B. Massachusetts C. Georgia D. Virginia
Slide253. The initial French exploration of NorthAmerica resulted in --- A. economic colonies in Florida B. competition with Spanish settlers C. plantations using slave labor D. cooperation with native groups
Slide264. The Treaty of Alliance of 1778 was signed bythe United States and ---- A. Spain B. Portugal C. Russia D. France
Slide275. Which factor contributed to colonial victory inthe American Revolution? A. Shortages of British troops B. Disloyalty of British generals C. Lack of British popular support D. Weakness of the British Navy
Slide286. The land area located between 800 W & 90 0 W and 25 0 N & 30 0 N represents the acquisition of --- A. Land won through the French & Indian War B. Territories according to the Northwest Ordinance C. Land as a result of the Revolutionary War D. Florida through a treaty with Spain
Slide297. The town meetings heldby colonists in buildings such as this one were important because they demonstrated a form of --- A. Religious toleration B. Direct democracy C. Multicultural integration D. Representative government Old South Meeting House, Boston
Slide308. The different types of economies found in theoriginal colonies were primarily a reflection of the --- A. Nationalities of the settlers B. Geography of the areas C. Provisions of the charters D. Religion of the settlers
Slide319. How did the Great Awakening most influencethe American Revolutionary movement? A. It supported the practice of slave labor B. It established official state religions C. It challenged the established government order D. It discouraged trade with foreign countries