AP Biology - Domain Eukarya: Kingdom Fungi

This AP Biology lesson covers the Domain Eukarya, specifically focusing on the Kingdom Fungi. Students will learn about the common ancestor of eukaryotes and the classification
- Uploaded on | 1 Views
-
 sarahbates
sarahbates
About AP Biology - Domain Eukarya: Kingdom Fungi
PowerPoint presentation about 'AP Biology - Domain Eukarya: Kingdom Fungi'. This presentation describes the topic on This AP Biology lesson covers the Domain Eukarya, specifically focusing on the Kingdom Fungi. Students will learn about the common ancestor of eukaryotes and the classification. The key topics included in this slideshow are . Download this presentation absolutely free.
Presentation Transcript
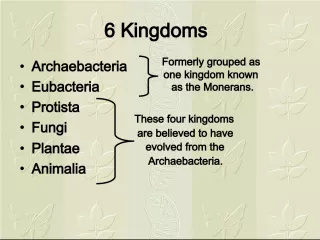
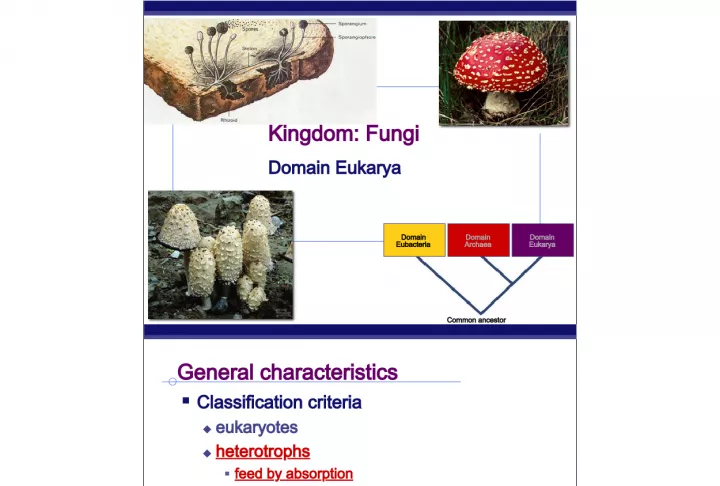
Slide1AP Biology2007-2008 Domain Eubacteria Domain Archaea Domain Eukarya Common ancestor Kingdom: Fungi Domain Eukarya
Slide2AP BiologyGeneral characteristics Classification criteria eukaryotes heterotrophs feed by absorption mostly multicellular except unicellular yeasts cell wall sexual & asexual reproduction So that’s 3 times cell walls have evolved: bacteria, fungi, plants
Slide3AP BiologyFungal Structure Fungal body mycelium thread-like cells hyphae Cells multiple nuclei Cell wall chitin polysaccharide + N just like crab shells
Slide4AP BiologyInternal structure Eukaryotic cells long, thread-like cells filamentous incomplete divisions between cells septum multiple nuclei septum chitin cell wall nuclei pore Aaaaah, structure–function relationship !
Slide5AP Biologyplant cell fungal hypha plant cell membrane plant cell wall Modes of Nutrition Heterotrophic secrete digestive enzymes feed by absorption parasites feeding on living creatures predators paralyzing prey decomposers breakdown dead remains Fungi live IN their food ! It’s like you living in Chocolate cake !
Slide6AP BiologyFungal Diversity Chytridiomycota Zygomycota Basidiomycota Ascomycota Fungi
Slide7AP BiologyEcological Roles Lichens are fungi that have discovered agriculture ! Decomposers recycle nutrients Symbiotic Relationships lichen fungi + algae cyanobacteria or green algae pioneer species in ecosystems makes soil from bare rock mycorrhizae fungi + plants live in & amongst plant roots enables plants to absorb more water & nutrients
Slide8AP BiologyMycorrhizae Critical role in plant growth extends water & nutrient absorption of roots without mycorrhizae with mycorrhizae Ectomycorrhiza Endomycorrhiza
Slide9AP BiologyReproduction Asexual budding in yeast Sexual spores spread by wind joining of + & – haploid spores haploid spores
Slide10AP BiologyAdult Offspring Gametes Zygote egg sperm diploid 2n haploid (n) meiosis fertilization mitosis & development mitosis & maturation male female
Slide11AP Biologyhypha (n) haploid (2n) diploid mating strain mating strain FUSION of + and – gametangia sporangium spores (haploid) MEIOSIS Zygomycete (Bread Mold) Life Cycle
Slide12AP BiologyBasidiomycete Life Cycle FUSION of and hyphae fruiting body MEIOSIS spores gills lined with basidia basidium zygote (n) haploid (n + n) dikaryotic strain strain 2 n (diploid)
Slide13AP BiologyFairy Rings
Slide14AP BiologyThe FIRST Antibiotics