Introduction to Anatomy: Understanding the Human Body


This chapter provides an orientation to the study of anatomy, which is concerned with exploring the structure and shape of the human body and its parts. It covers the different types of anatomy, including
- Uploaded on | 1 Views
-
 ashwini
ashwini
About Introduction to Anatomy: Understanding the Human Body
PowerPoint presentation about 'Introduction to Anatomy: Understanding the Human Body'. This presentation describes the topic on This chapter provides an orientation to the study of anatomy, which is concerned with exploring the structure and shape of the human body and its parts. It covers the different types of anatomy, including. The key topics included in this slideshow are . Download this presentation absolutely free.
Presentation Transcript
Slide1Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation
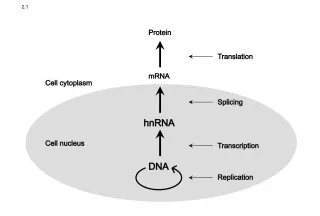
Slide2Anatomy – study of the structure and shape of the body and body parts and their relationship to each other Anatomy – study of the structure and shape of the body and body parts and their relationship to each other Gross anatomy – study of large, easily observable structures Gross anatomy – study of large, easily observable structures Microscopic anatomy – study Microscopic anatomy – study of very small structures of very small structures Physiology – study of Physiology – study of how the body and its how the body and its parts function parts function
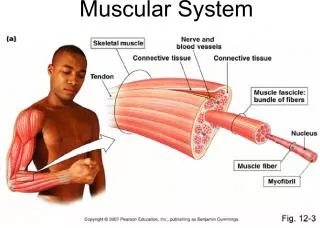
Slide3Structural organization Atoms>cells>tissues>organs>organ systems>organism Structural organization Atoms>cells>tissues>organs>organ systems>organism Organ systems Organ systems Integumentary Integumentary skin – waterproofs, cushions, protects skin – waterproofs, cushions, protects Skeletal Skeletal bones – support and protection bones – support and protection Muscular Muscular muscles – movement muscles – movement Nervous Nervous brain, spinal cord – fast control system brain, spinal cord – fast control system Endocrine Endocrine glands, hormones – slow control system glands, hormones – slow control system Cardiovascular heart, blood vessels – carries oxygen, nutrients Lymphatic lymph nodes, spleen – cleanse blood Respiratory lungs – supply oxygen Digestive stomach–breakdown and absorb food Urinary kidneys – rid body of waste Reproductive produce offspring
Slide4Necessary life functions Necessary life functions Maintaining boundaries Maintaining boundaries Movement Movement Responsiveness (irritability) – ability to sense changes in environment and react to them Responsiveness (irritability) – ability to sense changes in environment and react to them Digestion Digestion Metabolism – chemical reactions that occur w/in cells Metabolism – chemical reactions that occur w/in cells Excretion – removing excreta (wastes) Excretion – removing excreta (wastes) Reproduction Reproduction Growth – increase in size Growth – increase in size
Slide5Survival needs Survival needs Nutrients – chemicals used Nutrients – chemicals used for energy and cell building for energy and cell building Oxygen – energy reactions Oxygen – energy reactions require oxygen require oxygen Water – 60-80% of body weight Water – 60-80% of body weight Body temp maintained at about 37˚C (98˚F) Body temp maintained at about 37˚C (98˚F) Atmospheric pressure – breathing depends on appropriate pressure Atmospheric pressure – breathing depends on appropriate pressure Too low = lower gas exchange Too low = lower gas exchange
Slide6Homeostasis – body’s ability to maintain stable internal conditions Homeostasis – body’s ability to maintain stable internal conditions 2 main regulating systems: nervous, endocrine 2 main regulating systems: nervous, endocrine Homeostatic control mechanisms have 3 components Homeostatic control mechanisms have 3 components Receptor – responds to stimuli Receptor – responds to stimuli Sends info on by the afferent pathway Sends info on by the afferent pathway Control center – determines level at which a variable is to be maintained, analyzes info, and determines response Control center – determines level at which a variable is to be maintained, analyzes info, and determines response Sends info on by the efferent pathway Sends info on by the efferent pathway Effector – provides the means for a response Effector – provides the means for a response Negative feedback – slow/stop original stimulus – maintaining body temp Negative feedback – slow/stop original stimulus – maintaining body temp Positive feedback – speed up/start Positive feedback – speed up/start Ex. blood clotting, birth Ex. blood clotting, birth
Slide7Anatomical Position – body’s standard position (arms down with palms forward) Anatomical Position – body’s standard position (arms down with palms forward) See page 16-17 to review terms See page 16-17 to review terms
Slide8Directional terms (pg. 15) Directional terms (pg. 15) Superior (cranial) – head end Superior (cranial) – head end Inferior (caudal) – tail end Inferior (caudal) – tail end Anterior (ventral) – front, belly Anterior (ventral) – front, belly Posterior (dorsal) – back Posterior (dorsal) – back Medial – midline Medial – midline Lateral – outer Lateral – outer Intermediate – btw medial and Intermediate – btw medial and lateral lateral Proximal – close to limb attachment Proximal – close to limb attachment Distal – farther from limb attachment Distal – farther from limb attachment Superficial (external) – body Superficial (external) – body surface surface Deep (internal) Deep (internal)
Slide9Body planes and sections Body planes and sections Section – cut Section – cut Plane – imaginary line Plane – imaginary line where section is made where section is made Sagittal – lengthwise – Sagittal – lengthwise – divides into right and left divides into right and left parts parts Midsagittal – in half Midsagittal – in half lengthwise lengthwise Frontal – lengthwise – Frontal – lengthwise – divides into anterior and divides into anterior and posterior posterior Aka coronal section Aka coronal section Transverse – horizontal – Transverse – horizontal – divides into superior and divides into superior and inferior inferior Aka cross section Aka cross section
Slide10Body cavities Body cavities Dorsal body cavity Dorsal body cavity Cranial cavity Cranial cavity Spinal cavity Spinal cavity Ventral body cavity Ventral body cavity Thoracic cavity – lungs, heart Thoracic cavity – lungs, heart Mediastinum – separates lungs Mediastinum – separates lungs into right and left cavities – into right and left cavities – contains heart and trachea contains heart and trachea Abdominopelvic cavity Abdominopelvic cavity Abdominal cavity – stomach/liver Abdominal cavity – stomach/liver Pelvic cavity – repro./ bladder Pelvic cavity – repro./ bladder Divided into 9 regions (see pg 21) Divided into 9 regions (see pg 21) Umbilical – surrounding naval Umbilical – surrounding naval Epigastric – superior to umbilical Epigastric – superior to umbilical Hypogastric – inferior to umbilical Hypogastric – inferior to umbilical Right/left iliac (inguinal) – lateral to hypogastric Right/left iliac (inguinal) – lateral to hypogastric Right/left lumbar – lateral to umbilical Right/left lumbar – lateral to umbilical Right/left hypochondriac – lateral to epigastric Right/left hypochondriac – lateral to epigastric