Periodic Table Families: Predicting Properties and Behaviors of Elements


1PERIODIC TABLE FAMILIES The is a way of organizing information about elements amp atomic structure The Periodic Table PT is a way of organizing information about elements amp atomic structu
- Uploaded on | 6 Views
-
 aadijain
aadijain
About Periodic Table Families: Predicting Properties and Behaviors of Elements
PowerPoint presentation about 'Periodic Table Families: Predicting Properties and Behaviors of Elements'. This presentation describes the topic on 1PERIODIC TABLE FAMILIES The is a way of organizing information about elements amp atomic structure The Periodic Table PT is a way of organizing information about elements amp atomic structu. The key topics included in this slideshow are . Download this presentation absolutely free.
Presentation Transcript
Slide11PERIODIC TABLE FAMILIES The is a way of organizing information about elements & atomic structure The Periodic Table (PT) is a way of organizing information about elements & atomic structure in the PT help us predict properties of elements and how they will behave Groups and families in the PT help us predict properties of elements and how they will behave
Slide22GROUPS Elements that react similarly are in the same column called a group Elements that react similarly are in the same column called a group All elements in a group have the same number of valence electrons All elements in a group have the same number of valence electrons Groups are named by numbers Groups are named by numbers Groups that react similarly are called Groups that react similarly are called families
Slide33FAMILIES Groups that react similarly are called Groups that react similarly are called families be one column, or several columns put together Families may be one column, or several columns put together Families have names instead of numbers Families have names instead of numbers
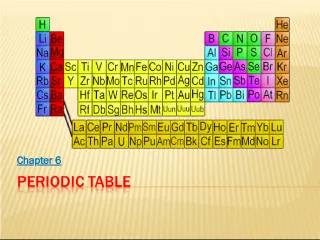
Slide44FAMILIES Alkali Metals Alkaline Earth Metals Transitions Metals (includes Lanthanide & Actinide series) Other Metals Metalloids Nonmetals Halogens Noble Gases EIGHT FAMILIES!
Slide5ALKALI METALS Group 1 (except H) 1 valence electron Very reactive metals, Always combined with another element in nature (like salt) Lowest ionization energy 2 nd lowest electronegativity
Slide6ALKALINE EARTH METALS Group 2 2 valence electrons Reactive metals Always combined with nonmetals in nature. Several are important mineral nutrients (such as Mg and Ca) 2 nd lowest ionization energy 3 rd lowest electronegativity
Slide7TRANSITION METALS Groups 3 - 12 2-7 valence electrons less reactive, harder, malleable good conductors of electricity Average ionization energy Average electronegativity
Slide8TRANSITION METALS:LANTHANIDES & ACTINIDES 1-2 Valence electrons Lanthanide all can be found in nature; only 1 radioactive Actinide all radioactive & only 90-92 occur naturally (others all “man-made”)
Slide9OTHER METALS 3, 4, or 5 Valence electrons Softer; lower boiling point than transition metals; 4 th highest ionization energy 3 rd highest electronegativity
Slide1010METALLOIDS (SEIMICONDUCTORS) 3,4,5,or 6 Valence electrons Acts like metal around non-metals; acts like non-metal around metals Has some, but not all the CHEMICAL properties of a metal Used for computer chips & solar panels
Slide1111NONMETALS 1, 4, 5, or 6 valence electrons Brittle; Poor conductors of electricity Common element in human body Necessary for life!! 3 rd highest ionization energy 2 nd highest electronegativity
Slide12HALOGENS Group 17 7 valence electrons Very reactive, volatile, diatomic, nonmetals Always found combined with another element in nature Used as disinfectants and to strengthen teeth 2 nd highest ionization energy Highest electronegativity
Slide13NOBLE/INERT GASES Group 18 8 valence electrons full valence energy levels make them VERY unreactive (inert), monatomic gases Used in lighted “neon” signs and in blimps Highest ionization energy Lowest electronegativity