The Cell Cycle and Mitosis


The cell cycle is a regular sequence of growth and division that cells undergo, which consists of six main parts: interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase,
- Uploaded on | 0 Views
-
 rosiesteward
rosiesteward
About The Cell Cycle and Mitosis
PowerPoint presentation about 'The Cell Cycle and Mitosis'. This presentation describes the topic on The cell cycle is a regular sequence of growth and division that cells undergo, which consists of six main parts: interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase,. The key topics included in this slideshow are . Download this presentation absolutely free.
Presentation Transcript
Slide1The Cell CycleMitosis
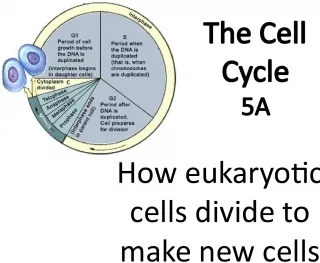
Slide2The Cell Cycle The regular sequence of growth and division that cells undergo.
Slide3The Cell Cycle 6 Parts Interphase Prophase* Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Cytokinesis • *When mitosis begins.
Slide4Stage 1: Interphase During interphase the cell grows, makes a copy of its DNA, and prepares to divide into 2 cells. Cell grows - The cell grows to full size and produces structures it needs. Copies DNA -Cell makes a full copy of the DNA. This process is known as replication. • DNA is found in the chromatin.
Slide5Stage 1: Interphase Preparing for Division - After replication has occurred, the cell copies its centrioles. • Centrioles - Cylindrical structures that produce microtubules used in mitosis.
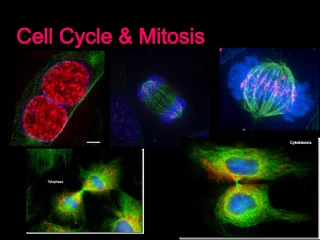
Slide6Stage 2: Mitosis Mitosis - The stage during which the cell’s nucleus divides into two new nuclei. During mitosis, one copy of the DNA is distributed into each of the two daughter cells. Daughter cells - The cells that are produced following cell division.
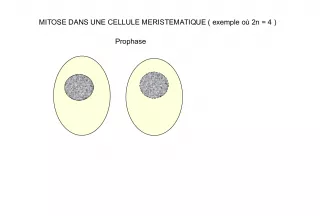
Slide7Stage 2: Mitosis Part 1 Prophase - Chromatin condenses in the nucleus to form chromosomes. • Chromosomes are made of chromatin. The two chromatids that make up a chromosome is held together in the center by a centromere. (make a diagram.) The centrioles move to opposite sides of the nucleus. The nuclear envelope breaks down.
Slide8Stage 2: Mitosis Part2 Metaphase - • Chromosomes line up across the center of the cell. • Each chromosome attaches to a spindle fiber at its centromere. • The spindle fibers are connected to the centrioles.
Slide9Stage 2: Mitosis Part 3 Anaphase - • The centromeres split, and the chromatids separate. • Each chromatid becomes a new chromosome. • New chromosomes move to opposite ends of the cell. • Cell begins to stretch out as the opposite ends are pushed apart.
Slide10Stage 2: Mitosis Part 4 Telophase - • Chromosomes lose their rod-like appearance • New nuclear envelope forms around the bundle of chromosomes. • Two halves separate even farther.
Slide11Stage 3: Cytokinesis Cytokinesis is the division of cytoplasm and organelles into each of the 2 new cells.
Slide12Stage 3: Cytokinesis During cytokinesis: Cell membrane pinches in around the middle of the cell. Cell splits in two and divides the cytoplasm. Each daughter cell has an identical set of chromosomes and about 1/2 the organelles. Cytokinesis leads back into interphase.
Slide13Stage 3: Cytokinesis Cytokinesis in PLANTS is different. A cell plate forms across the middle of the cell, which gradually develops into the new cell membranes. The new cell walls form around the cell membranes.
Slide14DNA Structure Double helix - Twisted ladder shape The sides of the ladder are made up of sugar molecules called deoxyribose, and alternate with a phosphate molecule. The rungs are made up of a pair of nitrogen bases. 4 nitrogen bases: adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C).
Slide15DNA Replication Process The DNA “ladder” unwinds and unzips, leaving 1 of the 2 nitrogen bases on either side of the “ladder”. Bases that are floating in the nucleus pair up with its appropriate partner. Adenine pairs with Thymine Guanine pairs with Cytosine